Quick version
Following a vegan or vegetarian diet can be healthy, but it's important to ensure you're getting all the necessary nutrients. A deficiency in key vitamins and minerals can lead to health issues such as fatigue, weakness, and more serious conditions like anemia or osteoporosis.
The most important nutrients to keep an eye on are:
- Vitamin B12: Primarily found in animal products. Vegans should take supplements or eat fortified foods.
- Iron: Found in legumes and nuts. Combine with vitamin C-rich foods for better absorption.
- Omega-3 Fatty Acids: Found in flaxseeds, chia seeds, and walnuts. Algal supplements are also an option.
- Calcium: Important for bone health. Found in leafy greens, tofu, and fortified plant-based drinks.
- Vitamin D: Necessary for calcium absorption. Supplements may be needed during the winter.
- Zinc: Important for the immune system. Found in legumes and whole grains.
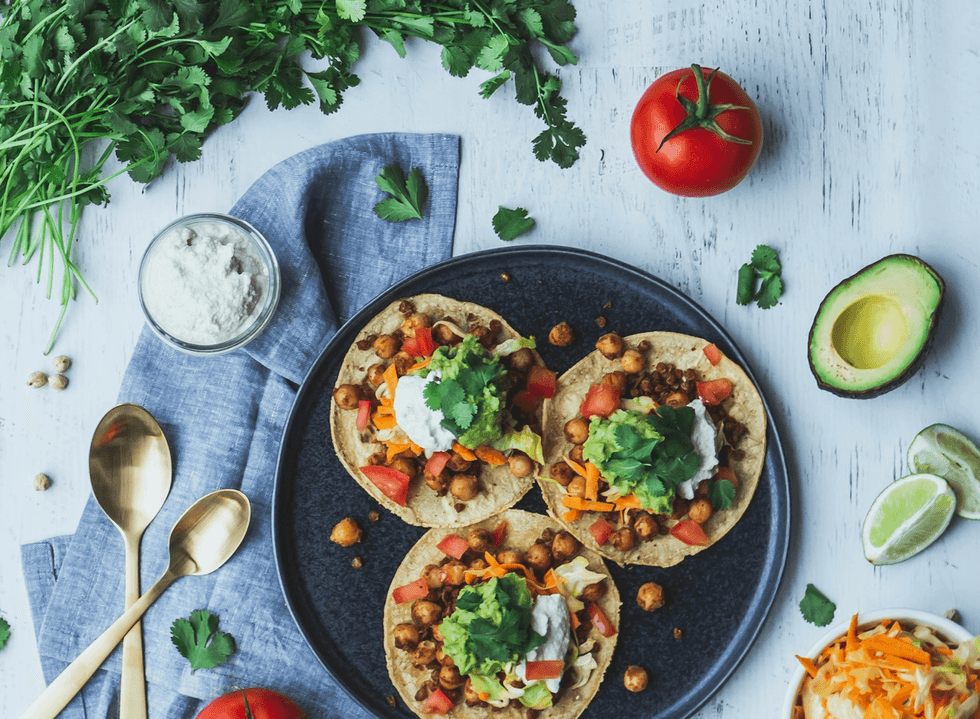
- Protein: Found in legumes, tofu, and nuts. Eat a varied diet to get all essential amino acids.
To ensure you're getting all the vital nutrients, consider regularly doing a vitamin and mineral test. It can help you understand if you need to adjust your diet or take supplements to avoid deficiencies.
7 important nutrients you as a vegan or vegetarian should be aware of
Vitamins, minerals, fatty acids, and protein are all crucial components for maintaining good health. A deficiency in these nutrients can lead to health problems such as fatigue, weakness, weakened immune system, and in some cases, more severe conditions like anemia due to iron deficiency, neurological issues from a lack of vitamin B12, or osteoporosis from calcium and vitamin D deficiencies. These conditions can significantly impact your health and may require medical treatment if not identified and addressed in time.
B vitamins
Vitamin B12 is perhaps the most talked-about nutrient when it comes to a vegan diet. B12 is vital for blood formation and nervous system function. Since vitamin B12 is primarily found in animal products, vegans may struggle to get enough of this vitamin. In fact, many people, including non-vegans and vegetarians, have levels that are borderline and indicate a deficiency. To ensure you are getting enough, it is recommended to take a B12 supplement or choose foods fortified with B12, such as certain plant-based drinks and breakfast cereals.
Folic acid, vitamin B9, is easy to obtain for vegans and vegetarians through plant-based foods like dark leafy greens, legumes, fruits, and fortified grains. It is particularly important for pregnant women or those planning to become pregnant, as it helps prevent neural tube defects in the fetus and contributes to normal blood formation and immune system function.
Iron
Iron is another critical nutrient, especially for women of childbearing age. Plant-based sources of iron, such as legumes, whole grains, nuts, and seeds, contain non-heme iron, which is not absorbed as efficiently as heme iron from animal products. To enhance the absorption of iron from plant-based sources, you can combine these with vitamin C-rich foods, such as citrus fruits, peppers, and broccoli.
Omega-3 fatty acids
Omega-3 fatty acids are important for brain function and heart health. The primary sources of omega-3 in a vegan diet are flaxseeds, chia seeds, and walnuts, as well as algal supplements. It is crucial to get enough of these fatty acids because they are necessary for various bodily functions.
Calcium
Calcium is needed for strong bones and teeth. While dairy products are a common source of calcium, there are also plant-based alternatives. Leafy greens, tofu, sesame seeds, and fortified plant-based drinks are excellent sources. For vegans, it is important to include these in your diet to ensure adequate calcium intake.
Vitamin D
Vitamin D is important for calcium absorption and bone health. During the winter months, when the sun's rays are not strong enough for us to produce vitamin D through our skin, a supplement may be necessary. Alternatively, you can use fortified products such as certain plant-based milk.
Zinc
Zinc is a mineral that plays a role in immune system function and wound healing. Vegan-friendly sources of zinc include legumes, whole grains, nuts, and seeds. Since plant-based foods contain phytic acid, which can inhibit zinc absorption, it is important to eat a varied diet to ensure sufficient intake.
Protein
Plant-based protein sources include legumes, tofu, tempeh, seitan, nuts, and seeds. It is important to eat a varied diet to get all the essential amino acids, although you do not need to consume them all at each meal.
How do you know if you are getting enough?
To ensure you are getting all the essential nutrients, we recommend regularly checking your levels through a vitamin and mineral test. Testing your levels can give you a clear picture of whether you need to make adjustments to your diet or supplement with certain nutrients. Such a test provides insight into what you need to eat more of to feel better and avoid potential deficiencies.
Remember, a well-planned vegan or vegetarian diet can be very healthy, but it requires you to be aware of your nutritional needs. If you are unsure whether your diet covers any specific nutrients, you can create your personalized test for vitamins and minerals, which can be a valuable tool to ensure you are getting everything you need.