Blood test to analyze the size variation of red blood cells
RDW (Red Cell Distribution Width) is a blood test that measures the size variation of your red blood cells (erythrocytes). Red blood cells play a crucial role in oxygen transport by carrying oxygen from the lungs to the body's tissues. The size distribution of the erythrocytes can provide valuable information about your blood count and can be an important factor in the investigation of anemia and other blood diseases.
Why should you test Erc(B)-RDW?
An RDW test provides a better understanding of your blood health and can be important for a complete blood analysis. The test is primarily used to:
- Detect and classify anemia: Variation in the size of your red blood cells can indicate different types of anemia, such as iron deficiency anemia, B12 deficiency anemia, or hemolytic anemia.
- Identify blood disorders and bone marrow involvement: Elevated RDW values can be linked to hematological diseases such as thalassemia, myelodysplastic syndrome, and certain types of bone marrow disorders.
- Understand your blood count: By analyzing the size variation of your erythrocytes, the test can provide deeper insight into how your body produces and processes red blood cells.
- Evaluate nutritional deficiencies: Changes in RDW can indicate deficiencies in important nutrients such as iron, folate, and vitamin B12, all of which are necessary for normal blood formation.
How is the Erc(B)-RDW test performed?
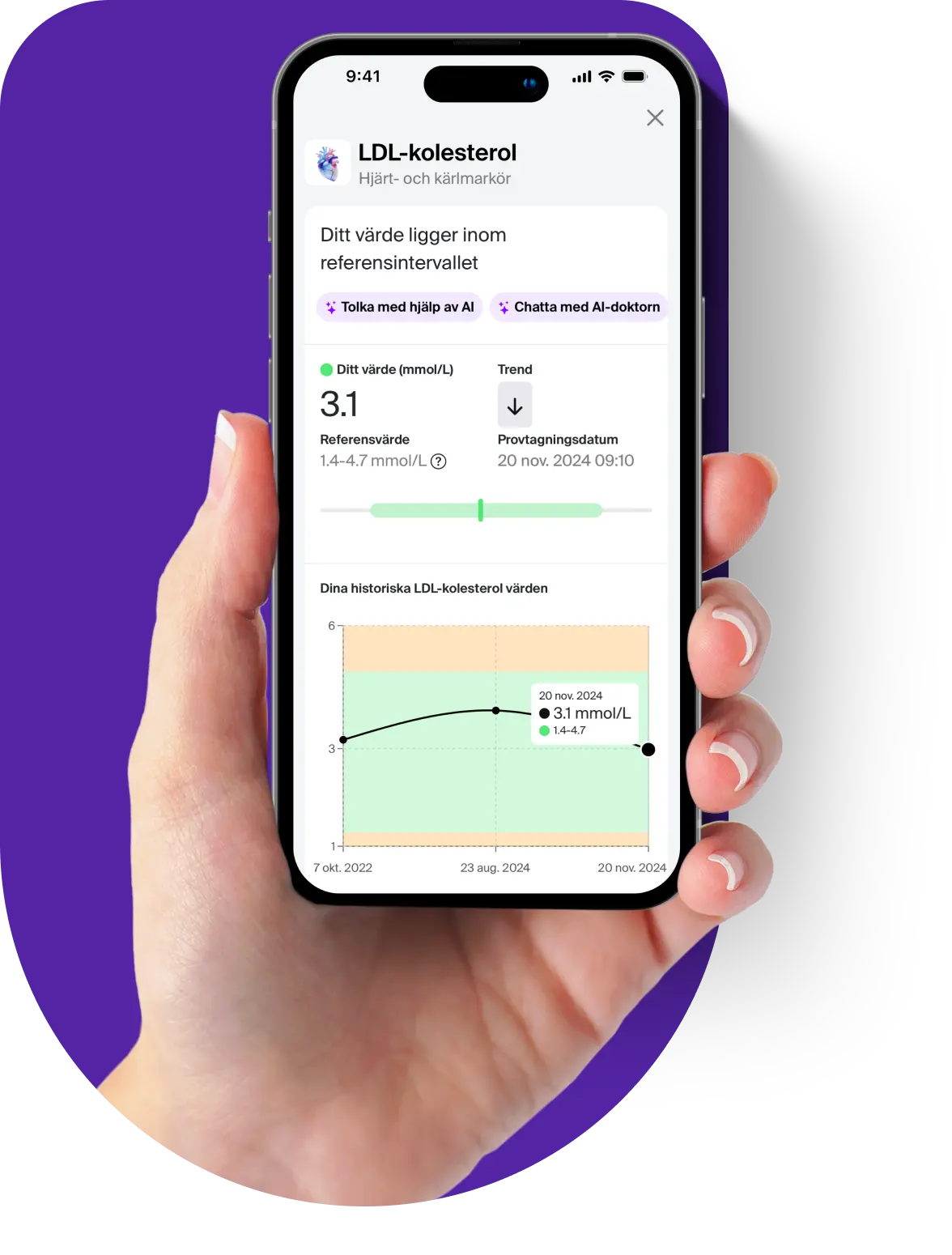
The test is performed through a blood sample where the size distribution of your red blood cells is analyzed. The result is often interpreted together with other blood status parameters such as B-MCV (mean cell volume), hemoglobin and hematocrit to provide a more complete picture of your blood health.
Knowing your RDW value can help you identify potential health problems at an early stage and, if necessary, take steps to improve your blood status and overall health.