NIPT test - prenatal screening
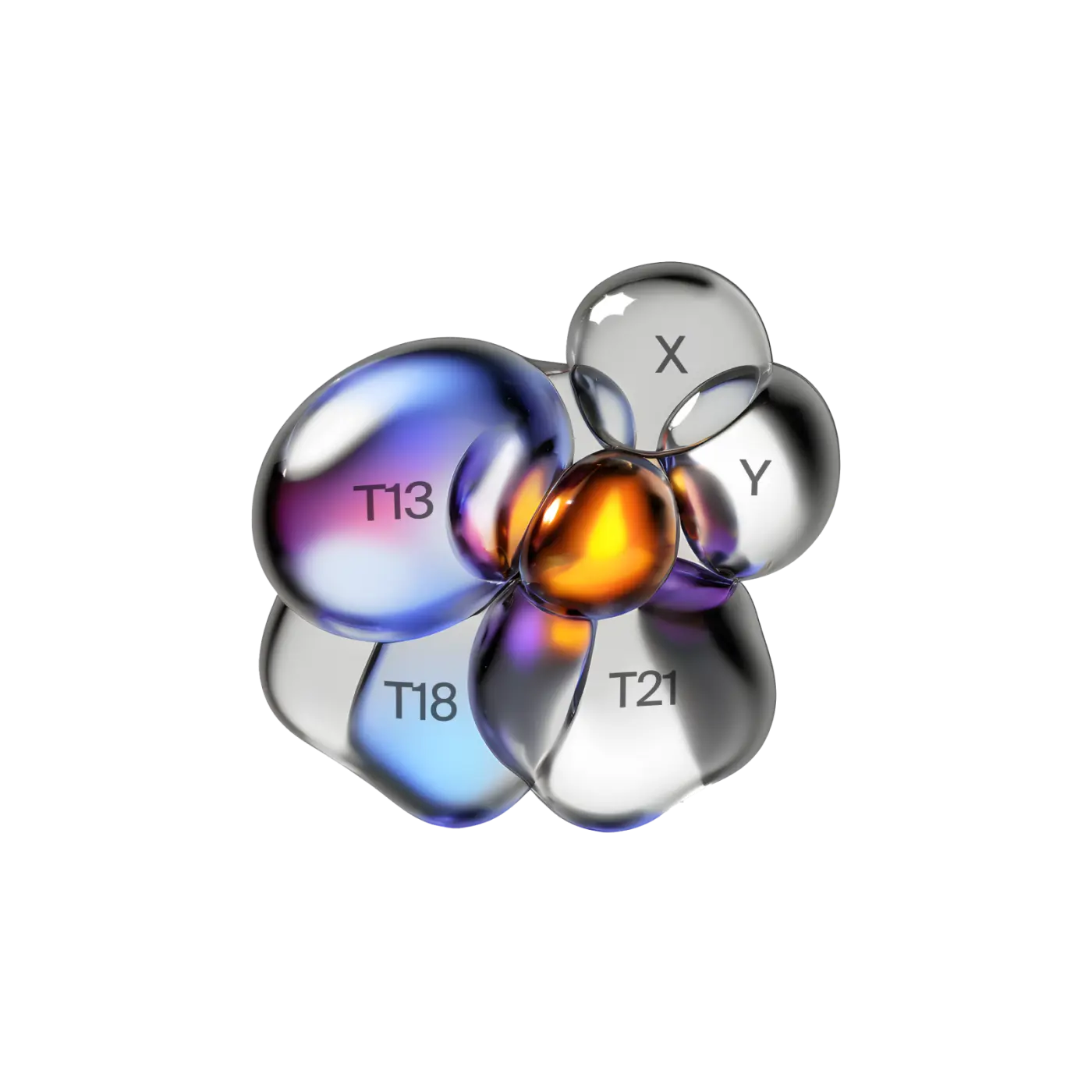
NIPT (Non-Invasive Prenatal Testing) is a blood test that allows for an early and safe assessment of the likelihood of chromosomal abnormalities in the fetus. By analyzing cell-free DNA from the mother's blood, NIPT can detect common aneuploidies such as trisomies 13, 18, and 21, as well as abnormalities in the sex chromosomes X and Y. NIPT is a simple blood test performed by healthcare professionals through a venous sample taken from the arm. You may experience slight soreness at the puncture site, but other side effects are rare. NIPT is highly reliable when no abnormalities are detected. If the NIPT test indicates an abnormality, follow-up tests such as amniocentesis or chorionic villus sampling (CVS) are recommended to confirm the result.
What does the NIPT test show?
NIPT assesses the probability of chromosomal abnormalities such as Down syndrome, Patau syndrome, and Edwards syndrome. NIPT is recommended when aneuploidy is suspected in the fetus, meaning abnormalities in the number of chromosomes. This analysis specifically targets the following markers:
- Trisomy 13 (Patau syndrome)
- Trisomy 18 (Edwards syndrome)
- Trisomy 21 (Down syndrome)
- Sex chromosome abnormalities (X and Y)
Test results are usually answered within 10 working days from the time the test was submitted.
When should the NIPT test be performed?
NIPT can be performed as early as pregnancy week 10+0. However, it is most commonly offered from week 12+0, when a first-trimester anatomical screening is conducted following recommendations from the Ultra-ARG (Ultrasound Diagnostic Working and Reference Group). This screening helps ensure the fetus is developing normally and can assist in identifying potential abnormalities.
How does NIPT work?
NIPT is conducted through massive parallel sequencing of cell-free DNA isolated from the mother's blood plasma. The analysis generates millions of short DNA sequences from both the fetus and the mother. If the fetus has an extra copy of one of the analyzed chromosomes (trisomy), there will be an increase in the number of DNA reads for that specific chromosome compared to reference chromosomes, enabling the detection of aneuploidies.
Benefits of NIPT
- Non-invasive: The analysis only requires a simple blood test from the mother.
- High accuracy: NIPT has a very high sensitivity and specificity for detecting trisomies.
- Early result: The test can be performed from week 10 of pregnancy, providing early information about the fetus's chromosomal makeup.
NIPT is a safe and reliable method for detecting chromosomal abnormalities in the fetus and can provide crucial information for further decision-making during pregnancy.
The expecting mother decides
The expecting mother always has the final decision on whether to undergo prenatal screening. It may be beneficial to discuss the matter with the other parent and aim for a joint decision. However, if that is not possible, it is ultimately the expecting mother who decides.