Do you experience symptoms that indicate hormonal imbalance? Common symptoms of hormonal imbalance in women are decreased sex drive, low energy levels, mood swings, hot flashes and night sweats, weight change, depression, menstrual disorders and digestive problems.
In case of hormonal imbalance, there is a disturbance among your hormones, which means that the body's processes are affected. The cause of the imbalance can be due to everything from age, diseases, diet, exercise and stress as well as other external factors.
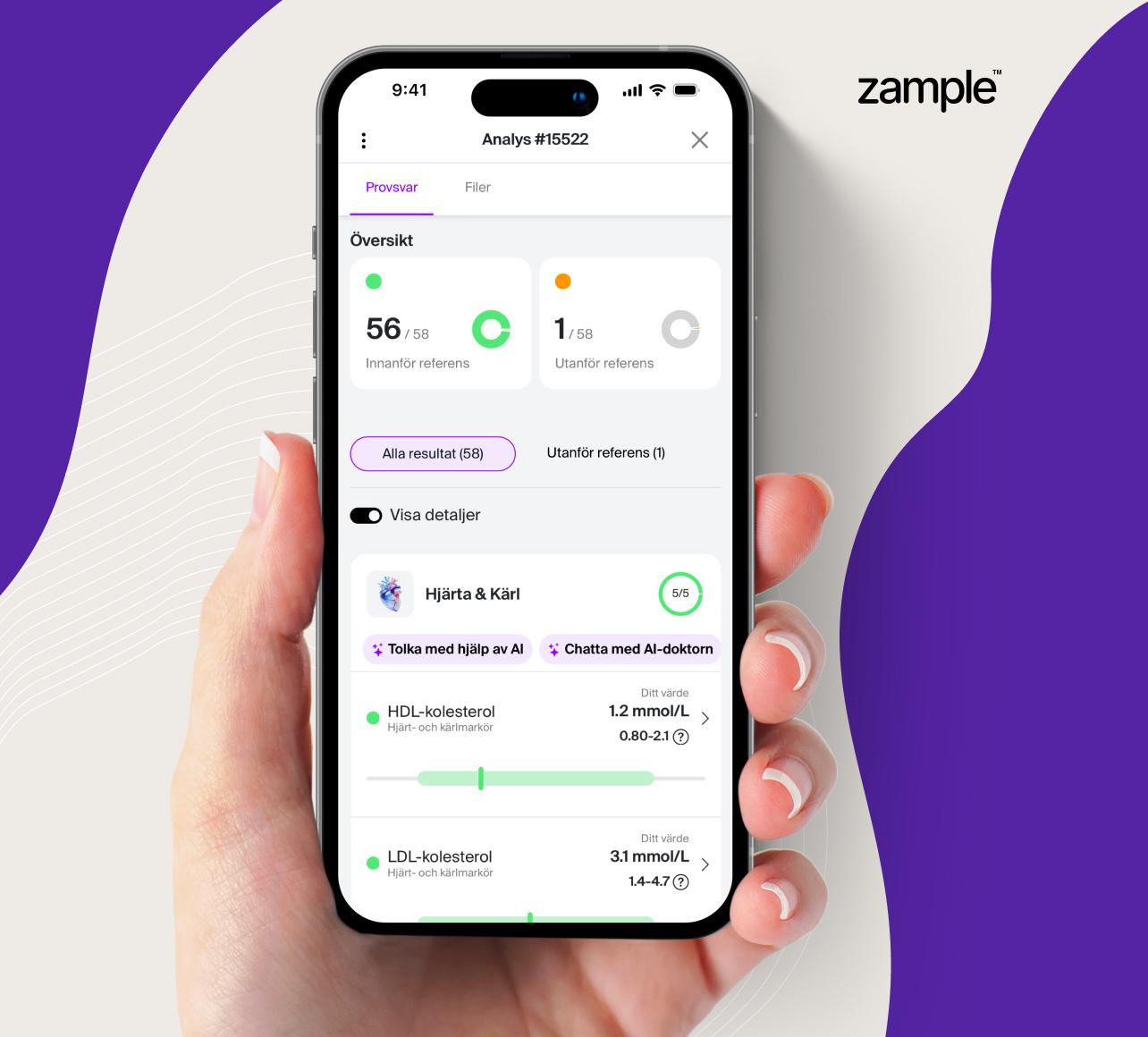
This is how the Hormonal balance health check can help you
By analyzing your hormone levels, you can gain deeper insight into why you experience symptoms and take control of your hormonal health and thus also increase your well-being.
Which hormones are tested in the Hormonal balance health check
Estradiol (estrogen)
Estradiol (E2) is the most important female sex hormone and a type of estrogen. It plays a crucial role in egg production, protects against bone loss, regulates cholesterol levels and affects the development of reproductive structures. As you age, E2 levels decrease, which can be an indication that you are in menopause. Imbalanced E2 levels can cause symptoms such as irregular periods, hot flashes, fatigue, headaches, sleep problems, anxiety, depression, low sex drive and worsening premenstrual syndrome (PMS).
Progesterone
Progesterone production drops significantly when a woman reaches menopause and ovarian function declines. This can affect the menstrual cycle and fertility. Progesterone is central to maintaining reproductive health and is of particular importance during the fertile period in women who may become pregnant.
Follicle stimulating hormone (FSH)
Follicle stimulating hormone (FSH) has an important function in the regulation of the menstrual cycle and plays a central role in egg production and ovulation. Imbalanced FSH levels can negatively affect fertility. High FSH levels may indicate that a person is in menopause, where the ovaries gradually lose their ability to produce eggs. It is important to monitor and balance FSH levels to maintain healthy reproductive function.
Luteinizing hormone
Luteinizing hormone (LH) plays a crucial role in reproduction. During the middle of the menstrual cycle, LH levels increase, resulting in ovulation when the ovaries release an egg. Imbalanced LH levels can lead to irregular periods and difficulty conceiving. High LH levels can indicate menopause.
The thyroid hormones T3, T4 and TSH
The thyroid gland regulates metabolism. The hormones T3 and T4, produced by the thyroid gland, affect weight, energy, mood and bone health. Thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH) regulates hormone production. Testing of TSH, T3 and T4 can identify imbalances and thyroid problems.
When should I submit the blood sample?
In case of both regular and irregular menstruation, we recommend that you carry out the sampling on day 3 of your menstrual cycle (day 1 is your first bleeding day).
If you no longer have your period, you can submit the blood sample at any time.