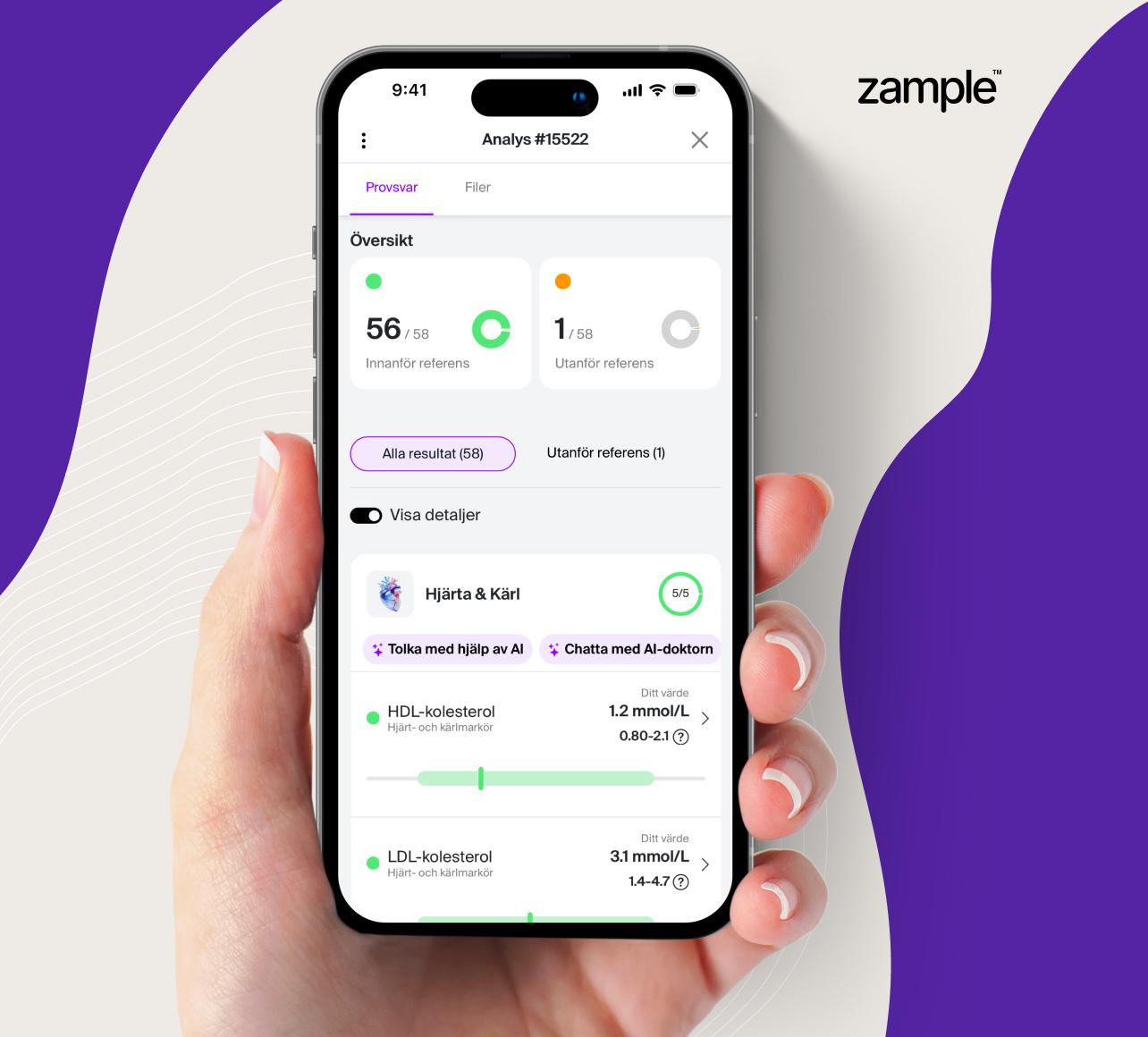
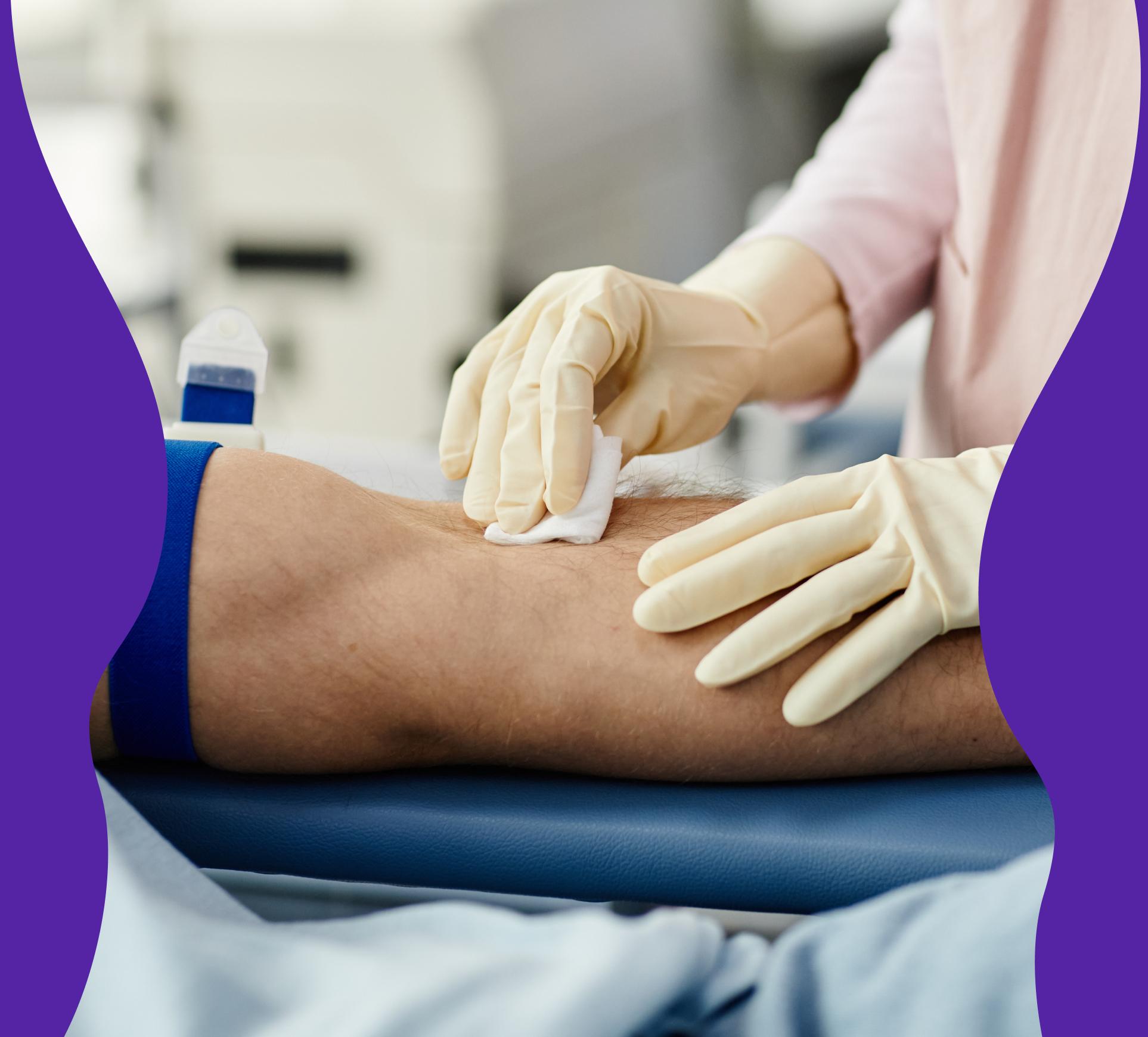
It may be appropriate to test your estrogen and progesterone levels if you experience symptoms of hormonal imbalance, such as for example:
- irregular menstrual cycles
- heavy bleeding
- mood swings
- sleep disorders
- hot flashes
- reduced sex drive
It may also be appropriate to test the hormone levels if you feel that you are having difficulty getting pregnant or maintaining a pregnancy.
It is important to note that hormone levels can vary during the menstrual cycle, so it is best to take the sample at a specific time in the cycle to get a more accurate picture of hormone levels. Usually the blood test is taken on days 19-21 of a 28-day cycle, but it can vary depending on the length of your cycle.
The balance between estrogen and progesterone levels varies depending on the woman's age and menstrual cycle. During the first half of the menstrual cycle, estrogen levels gradually increase to reach their peak just before ovulation. After ovulation, estrogen levels drop and progesterone levels rise to prepare the uterus for possible pregnancy. If pregnancy does not occur, both estrogen and progesterone levels drop again, triggering menstruation.
The balance between estrogen and progesterone is important for a healthy menstrual cycle and fertility. A balanced level of estrogen and progesterone is necessary for ovulation to occur and to maintain a pregnancy.
As age and state of health play a role in the assessment of hormonal imbalance, the ratio of the estrogen and progesterone value is not calculated. For investigation of hormonal imbalance, we recommend that you contact your doctor or health centre.
Here you can read more about reference values for estrogen (estradiol) and progesterone.