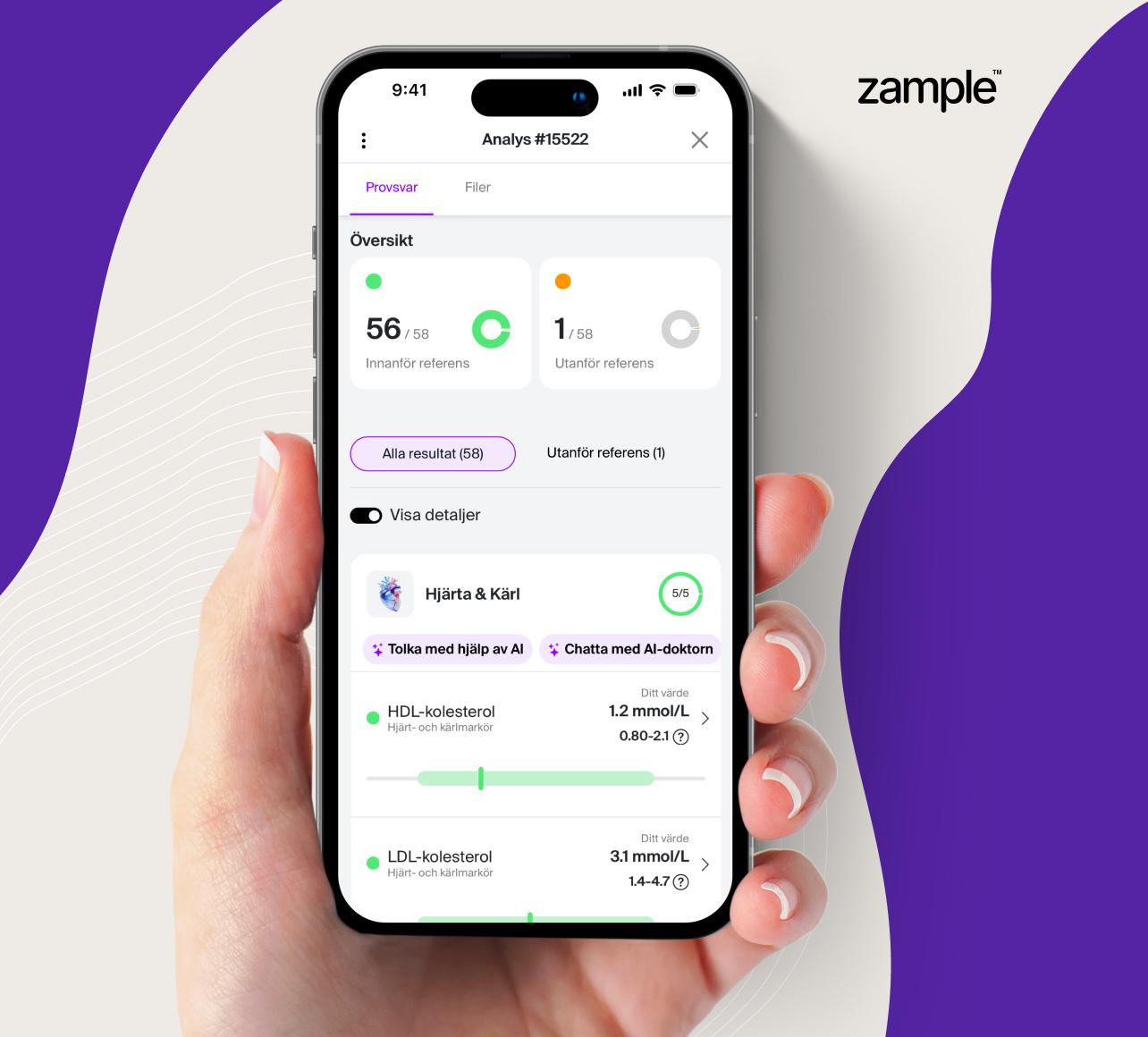
P-Myoglobin is a test to measure the concentration of myoglobin in the blood, an oxygen-binding protein found in cardiac and skeletal muscle. Myoglobin is released into the bloodstream upon muscle injury, making it an early marker for heart attack and other muscle-related injuries. The test is particularly useful for quickly identifying muscle injuries, as elevated levels may indicate serious conditions such as heart attack, rhabdomyolysis, or acute muscle damage.
Purpose of Myoglobin Testing
P-Myoglobin tests are used to identify muscle injuries and assess their extent, particularly in individuals at risk of heart attack or severe muscle trauma. This test is an essential part of emergency care to detect heart attacks before other cardiac markers, such as Troponin, become detectable. P-Myoglobin can also be used to monitor individuals at risk of rhabdomyolysis, where elevated levels may place a strain on the kidneys.
What do elevated myoglobin levels indicate?
Elevated levels of myoglobin can indicate muscle injury caused by heart attack, intense physical exertion, trauma, or conditions like rhabdomyolysis. In such cases, myoglobin is released from muscles into the bloodstream, where high levels can have serious consequences for the kidneys.
Are low myoglobin levels clinically significant?
Low levels of myoglobin are usually not clinically significant and often indicate the absence of acute muscle injury. This makes the myoglobin test particularly useful for identifying acute injuries rather than as a test for general health check-ups.