Troponin T - A blood test for suspected heart muscle injury
Heart muscle injury related to a heart attack is a serious condition that requires rapid diagnosis and treatment. Troponin is a protein released into the bloodstream when the heart muscle is damaged, making troponin analysis a common procedure when a heart attack or other heart muscle injury is suspected. Elevated troponin levels can be detected just a few hours after heart muscle damage, making it a valuable blood test for the early detection and management of potential heart problems.
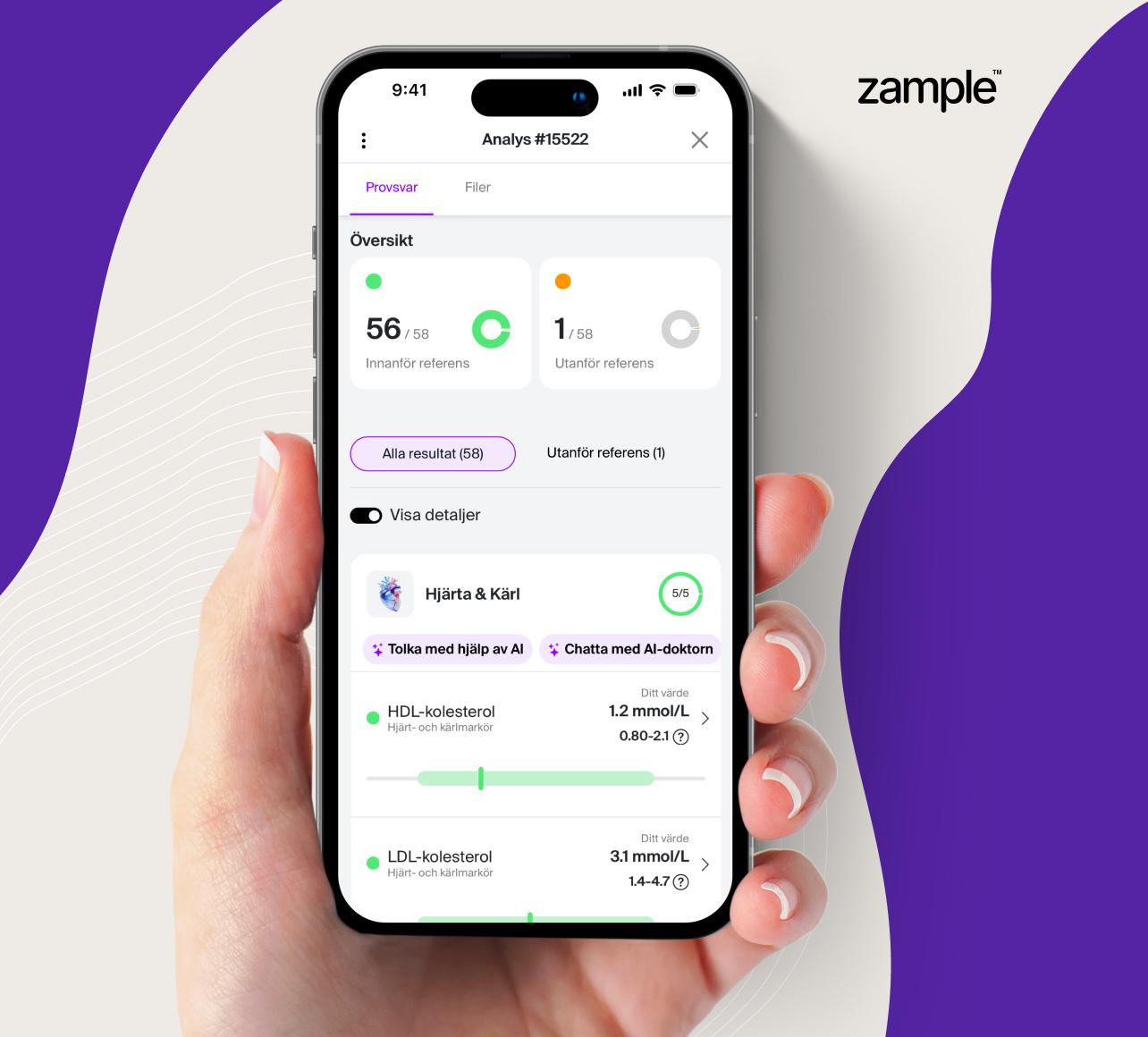
The troponin test measures the concentration of this protein in the blood and is used to confirm or rule out heart muscle injury.
Elevated troponin levels indicate damage to the heart muscle, while normal levels can help rule out heart muscle injury. This makes the troponin test a crucial tool in emergency care for identifying heart attacks and other cardiac issues.
Advantages of the Troponin test:
- Early detection of heart muscle injury: P-Troponin T can help detect heart muscle damage early, enabling prompt treatment and reducing the risk of complications.
- High sensitivity: The test is highly sensitive and can detect even small injuries to the heart muscle, improving diagnostic accuracy.
- Effective follow-up: The test can be used to monitor heart recovery and assess treatment responses in patients with known heart damage.
- Rapid diagnosis: An elevated Troponin T level can quickly confirm heart muscle damage, reducing the need for further invasive investigations.
Interpreting test results
When a doctor interprets your test results, elevated troponin levels may indicate heart muscle damage. This may not only be due to a heart attack but also other heart conditions such as myocarditis, arrhythmias, valvular disease, or cardiomyopathy. Additionally, other conditions like kidney problems, lung issues, or severe infections such as sepsis can affect troponin T levels in the blood.
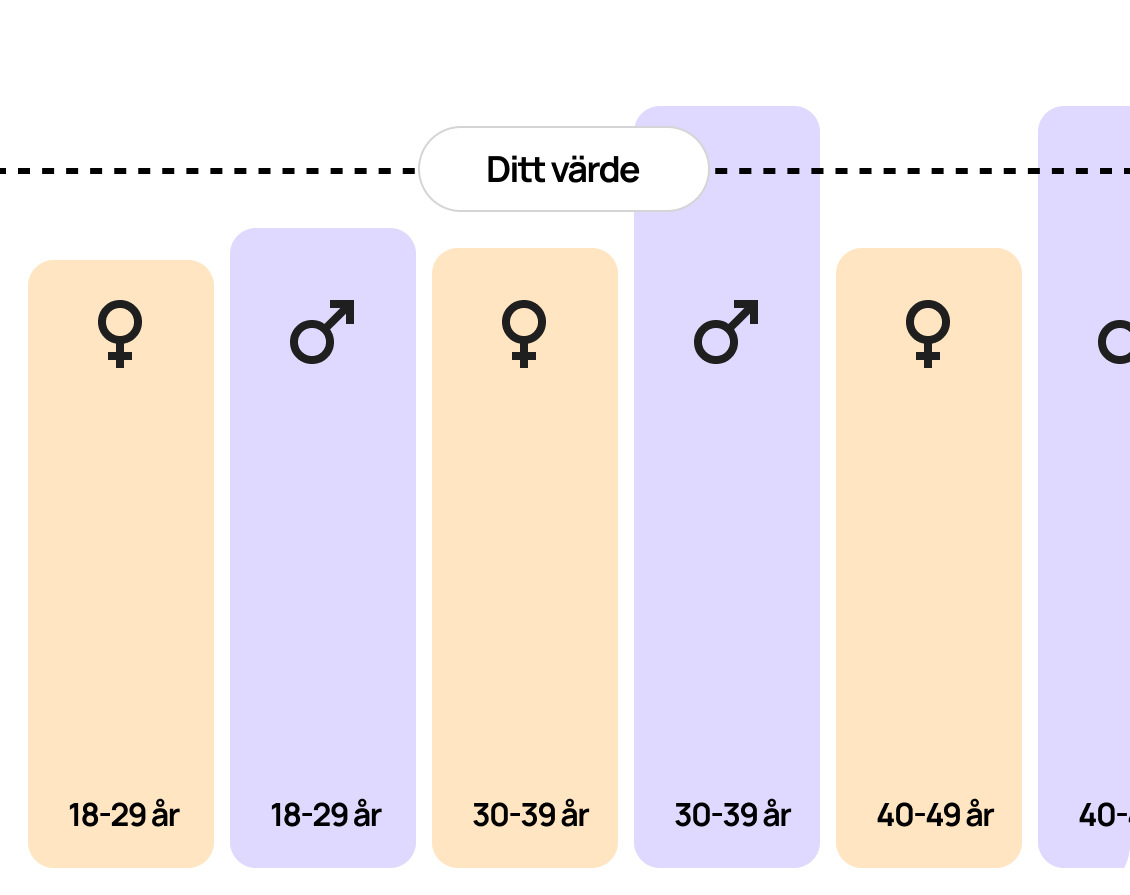
Reference range for P-Troponin T
Elevated concentrations refer to test results over 15 ng/L.
The decision threshold for acute myocardial injury is considered above 14 ng/L.
What is myocardial injury?
Myocardial injury refers to damage to the heart muscle, also known as the myocardium. The heart muscle is responsible for pumping blood throughout the body, and damage can severely impact the heart's ability to function. Myocardial injury can occur in various conditions but is often associated with a heart attack (myocardial infarction), where a blood clot blocks blood flow to the heart, leading to oxygen deprivation and damage to the heart muscle.
Besides heart attacks, myocardial injury can be caused by other conditions such as:
- Myocarditis (inflammation of the heart muscle)
- Heart failure
- Ischemic heart disease (poor blood flow to the heart)
- Trauma or surgical interventions involving the heart
During myocardial injury, proteins such as troponin are released from the heart muscle cells, leading to higher concentrations in the bloodstream.
It is important to note that doctors cannot diagnose heart muscle damage based solely on the blood test. A complete diagnosis requires additional examinations, such as an ECG or echocardiogram, as well as a comprehensive evaluation of your medical condition. Based on your test results, you will learn whether your value is within the normal reference range or if further medical attention is recommended.