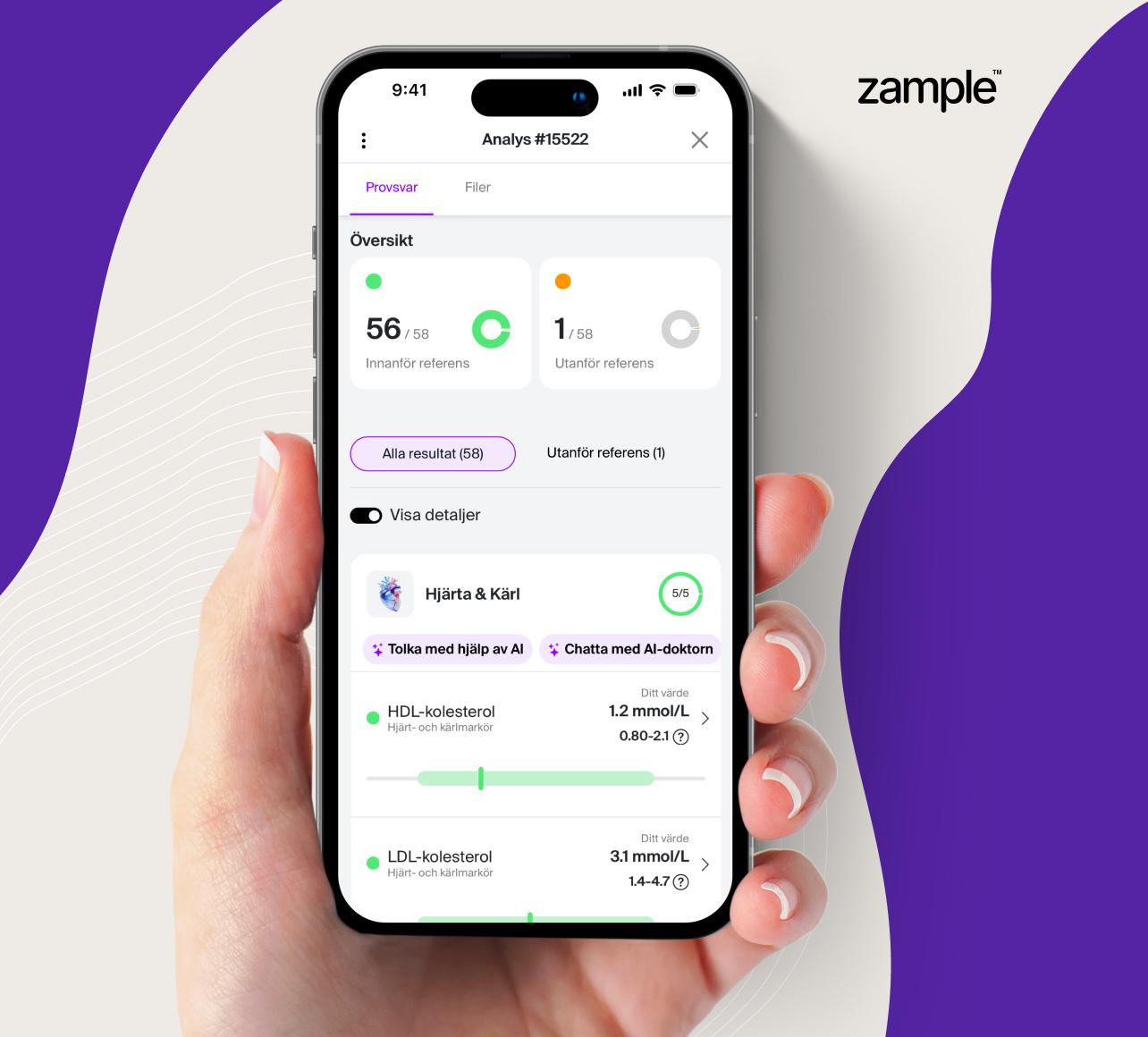
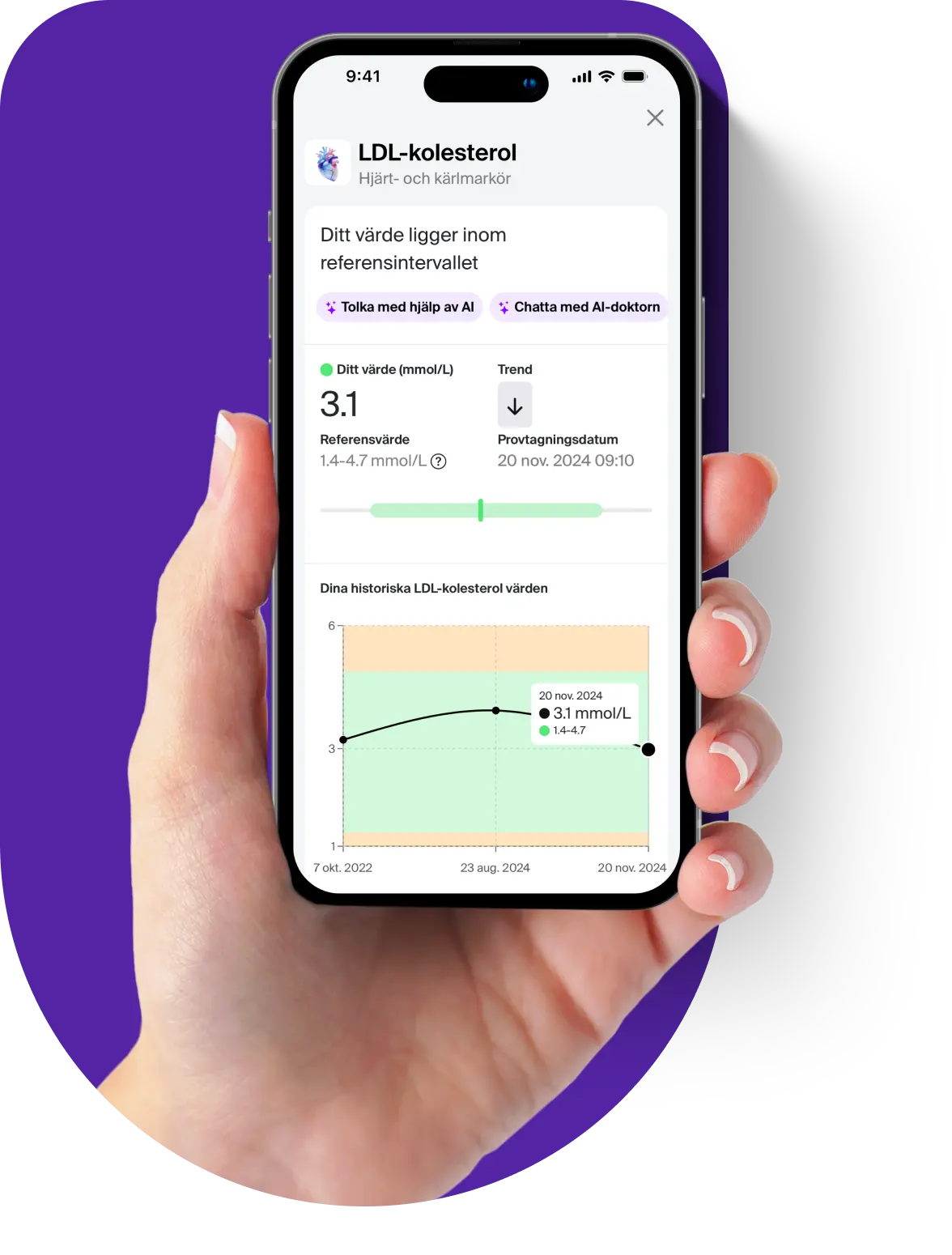
The cortisol test measures your levels of the stress hormone cortisol in your blood. Cortisol is a hormone that is also called the body's stress hormone and is produced in the adrenal glands. By testing you, you find out if your body produces too much or too little cortisol, which in turn can give rise to possible symptoms.
When you are designated for physical or mental stress, the body's production of cortisol is affected in order for you to perform better both physically and mentally. Cortisol helps the body regulate the metabolism of fat, proteins and sugar in the body. Cortisol also inhibits inflammation and allergies. At too high levels of cortisol, it can cause, among other things, sleep problems, and at too low levels you can experience, for example, fatigue, anxiety, weight gain, weight loss and muscle weakness.
Symptoms or discomfort with abnormal cortisol levels
Elevated cortisol levels can indicate conditions such as Cushing's syndrome, which can cause symptoms such as:
- Weight gain
- Round face shape
- High blood pressure
- Muscle and bone weakness
- Impaired immune system
Low cortisol levels may indicate Addison's disease or secondary adrenal insufficiency, and may lead to symptoms such as:
- Chronic fatigue
- Weight loss
- Low blood pressure
- Muscle weakness
- Anxiety
Cortisol levels in the blood vary during the day, and therefore it is important to take into account the time of sampling.
Reference range for S-cortisol
Reference range for cortisol, note that cortisol has a diurnal variation:
- Morning test: 145 – 620 nmol/L
- Afternoon test: 95 – 460 nmol/L
A non-stressed morning test for S-cortisol above 350 nmol/L usually contradicts cortisol deficiency.