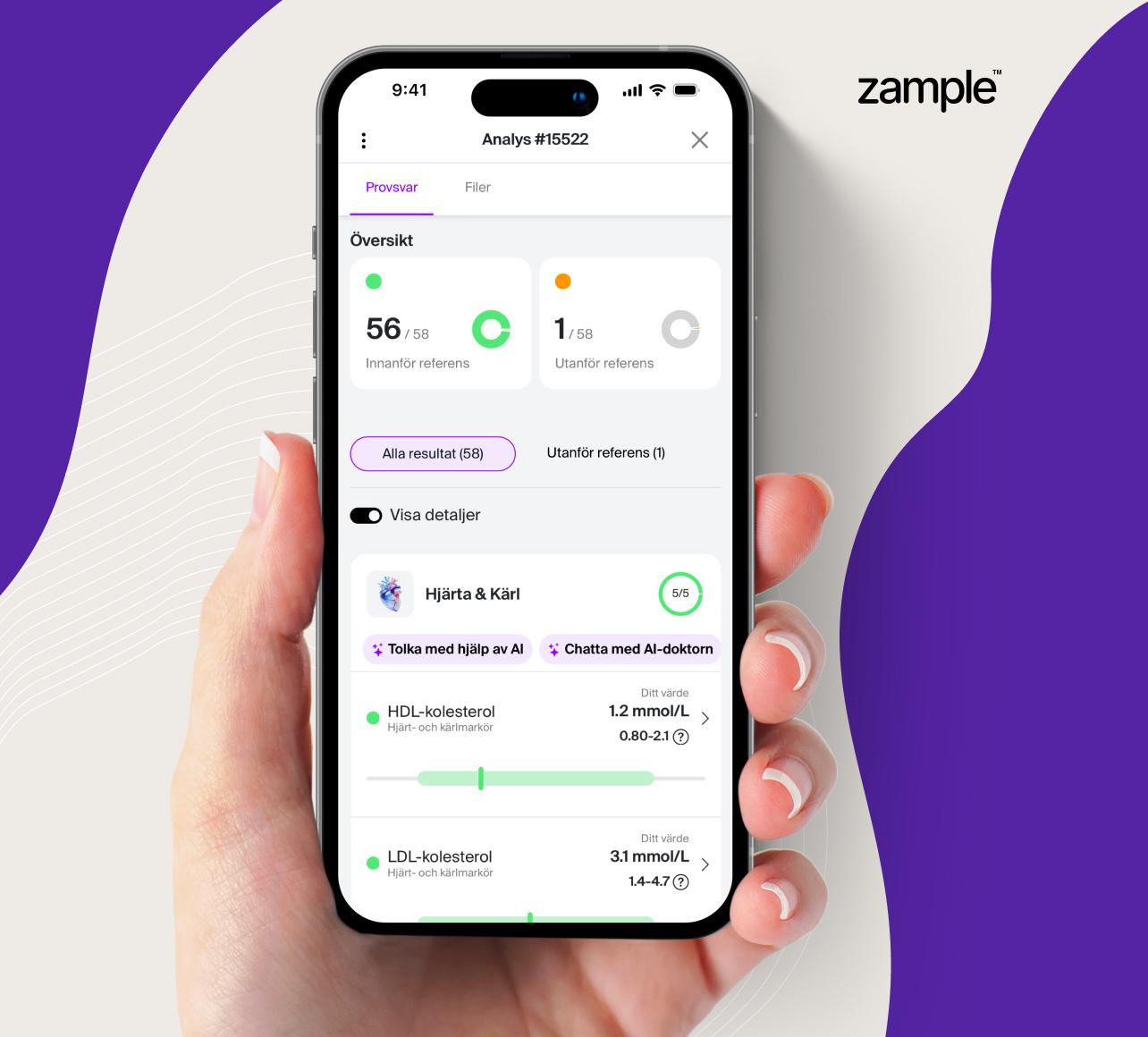
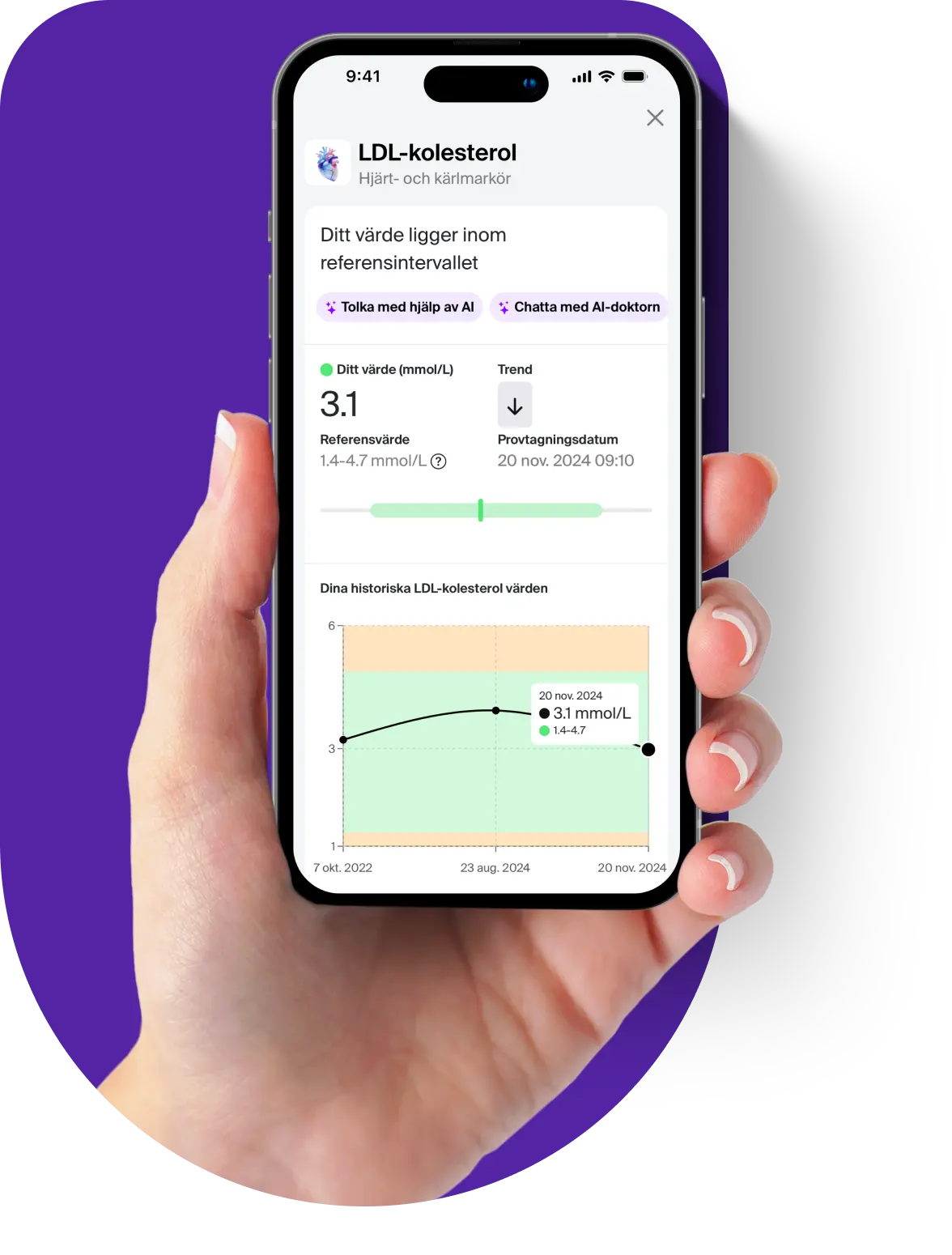
Estradiol is an estrogen hormone produced in the ovaries and is primarily related to women's health and fertility. Through an estradiol test, you can gain a better understanding of your hormonal balance and at the same time more knowledge about your fertility. It should be added that estradiol is also formed in the testicles of men, although in significantly lower concentrations.
Estradiol levels in the blood vary greatly during the menstrual cycle, with higher estradiol levels occurring during ovulation. During pregnancy, estradiol levels increase dramatically to support fetal development.
Estradiol is relevant to analyze because the hormone helps regulate cholesterol levels, maintain bone strength and improve your mood. Low levels of estradiol can cause symptoms such as vaginal dryness, hot flashes, difficulty sleeping and reduced sex drive. By testing your estradiol levels, you can obtain valuable information about your reproductive health that may be relevant in several clinical contexts. Here are some common reasons why women test their estradiol levels;
- Fertility assessment, Measuring estradiol levels can be used in fertility assessments to monitor ovarian function and assess whether there are sufficient estradiol levels for a normal menstrual cycle.
- Menstrual cycle regulation, Testing estradiol can be part of the assessment of a regular menstrual cycle.
- Menopause and transition, Measuring estradiol levels can be used to monitor the transition to menopause and may be useful in conjunction with hormone replacement therapy (HRT) if it is being considered.
- Assessment of hormone therapy, For women undergoing hormone therapy, particularly those receiving estrogen replacement therapy (ERT) or an intrauterine device, measuring estradiol levels may be useful.
- Ovulation prediction, Measuring estradiol can be used as part of the prediction of ovulation for women considering pregnancy.
- Assessing health effects, testing estradiol levels can help evaluate the health effects of hormonal balance.
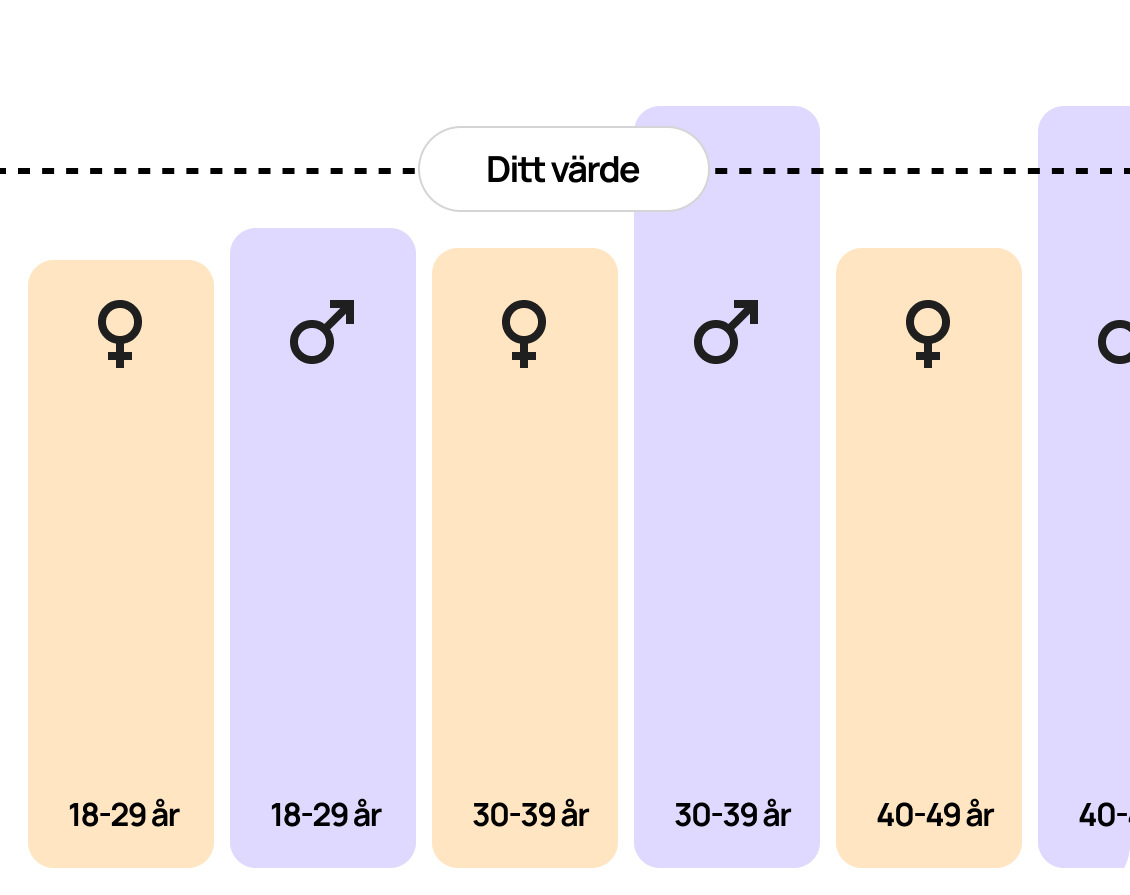
Estradiol Reference Range
Estradiol levels vary depending on the phase of the menstrual cycle a woman is in, as well as her age and hormonal status. Here are common reference ranges for women:
- Follicular phase (days 1-14): 100–650 pmol/L
- Midcycle phase (ovulation): 230–1300 pmol/L
- Luteal phase (days 15-28): 200–850 pmol/L
- Postmenopause: Lower than 120 pmol/L
Men typically have significantly lower estradiol levels, with a reference range below 160 pmol/L.
How estradiol levels change during the menstrual cycle
During the menstrual cycle, estradiol levels are affected by the interaction of several hormones. They are usually lowest at the beginning of the cycle (follicular phase) and begin to rise until ovulation, when they reach their highest level. After ovulation (luteal phase), estradiol levels gradually fall again, provided that pregnancy does not occur. For postmenopausal women, levels are generally low because ovarian function is declining.
Why should you have an estradiol test? Here are the most common reasons
- Hormone balance: Helps evaluate the body's hormonal status, especially estrogen levels.
- Fertility: Used in fertility studies and to assess ovarian function and ovulation.
- Menopausal symptoms: Provides information about the transition phase and can guide possible hormone replacement therapy.
- Symptom assessment: Can explain symptoms such as sleep problems, mood swings, osteoporosis, and decreased libido.
- Health assessment: Estradiol levels are important for understanding risks related to cardiovascular health and bone health.
- Combined analysis: Often recommended along with FSH, LH, and progesterone for a complete hormonal profile.