GT (Gamma-Glutamyltransferase) – Venous blood test for liver and biliary function
GT, or Glutamyltransferase as it is called, is an enzyme. GT is measured when liver or biliary tract diseases are suspected. When investigating suspected liver disease, more markers are also measured to obtain liver values.
Elevated GT values are seen in liver and biliary diseases, liver damage by alcohol and also due to certain medications. However, isolated elevated GT values have low disease specificity and should always be assessed in combination with other liver tests and any medical history.
Moderately elevated GT levels can be seen in, for example, infectious hepatitis, diabetes and obesity. Higher values may indicate more serious conditions such as biliary tract obstruction, liver metastases or pancreatic diseases. Since many factors can affect the GT level, it is important that the interpretation of the test result is based on a comprehensive assessment of the patient's clinical situation.
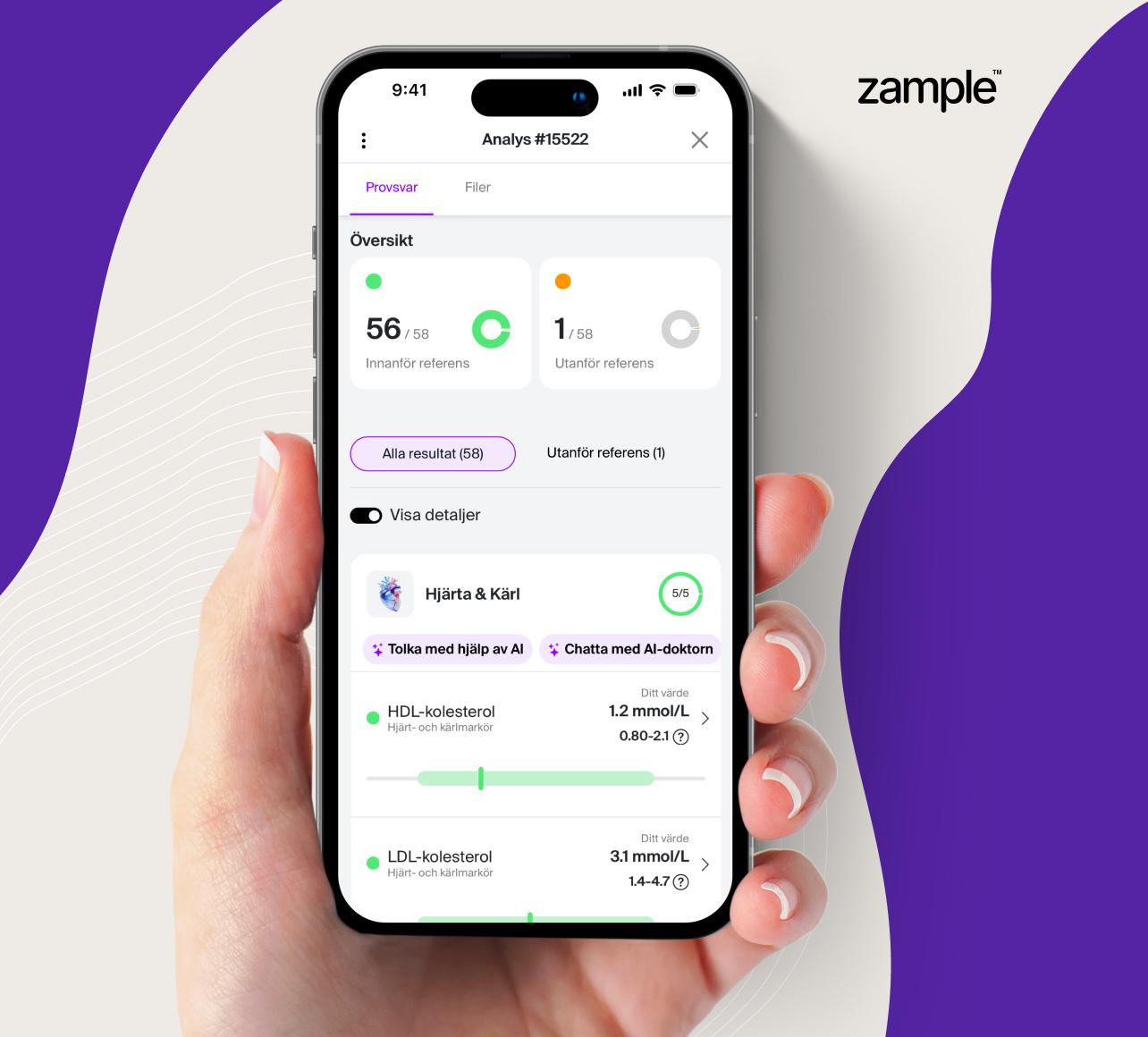
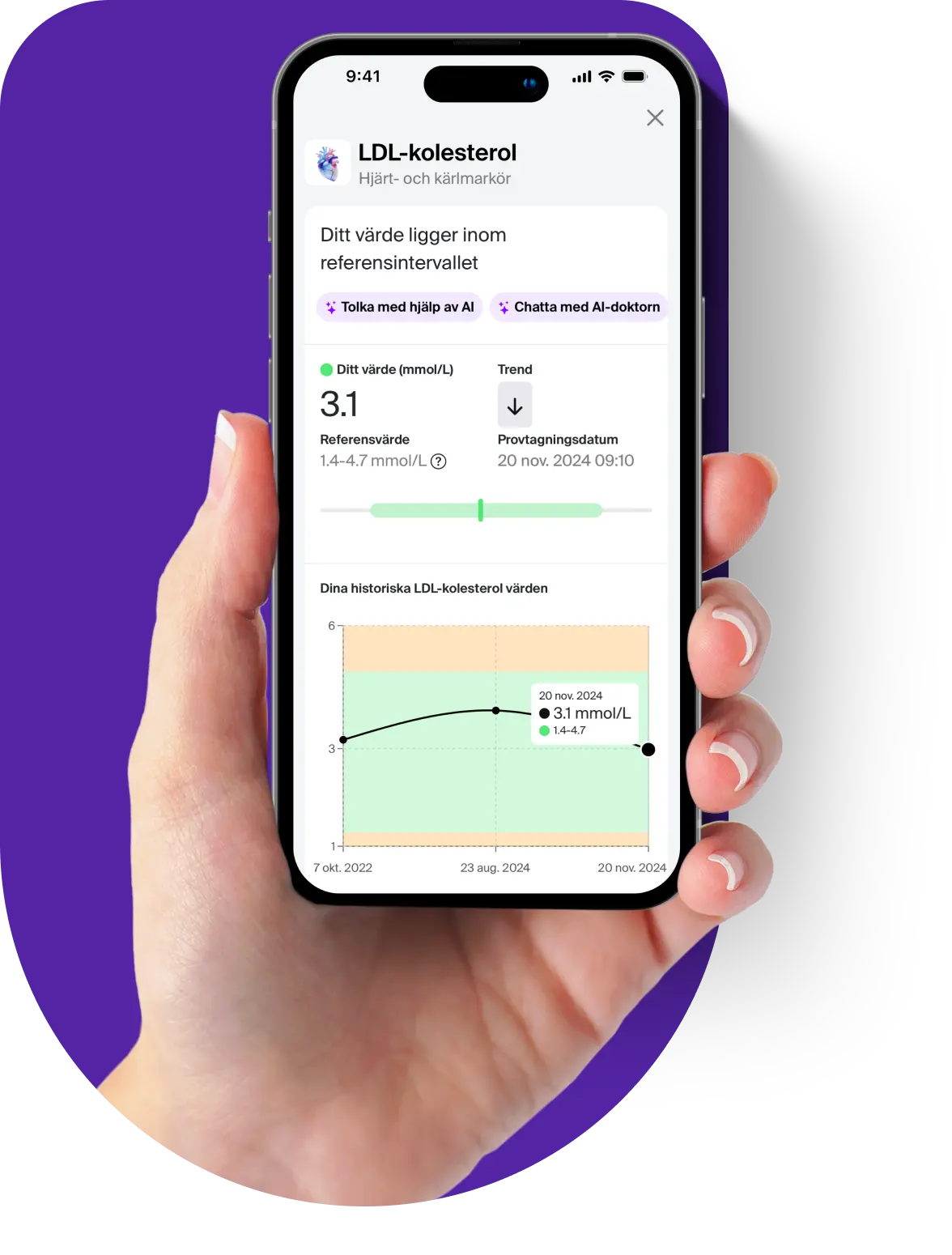
Interpretation of test results for P- GT, gamma
When interpreting GT values, it is crucial to take into account both the test result and the clinical picture. Elevated levels of GT can have different causes depending on the individual's health status and lifestyle. To determine the underlying cause of elevated values, the doctor needs to take into account the patient's symptoms, medical history, and any medications or alcohol use.
For example, if alcohol-related liver damage is suspected, GT levels may be markedly elevated, while other liver diseases such as hepatitis or cirrhosis often require a more comprehensive analysis of other liver tests such as AST, ALT, and bilirubin. It is also important to consider other factors such as medication use, as some medications can affect GT levels without necessarily having an underlying disease.
Elevated GT values can sometimes also be seen in conditions that do not directly affect the liver, such as heart failure, diabetes or obesity. Therefore, it is important for the doctor to make a careful overall assessment of all relevant factors in order to make a correct diagnosis and take appropriate measures. In some cases, further examinations such as ultrasound or liver biopsy may be necessary to obtain a complete picture of the patient's health status.