Our ferritin test measures your iron level and can detect if you have an iron deficiency. Ferritin is analyzed to give you a deeper insight into the body's iron stores. Through a ferritin test, you can discover if your body has an iron deficiency by analyzing levels of ferritin. Ferritin is a protein in the body that binds iron. Your amount of ferritin in your blood shows how much iron you have stored in your body. A lack of iron often leads to, among other things, lack of energy and fatigue.
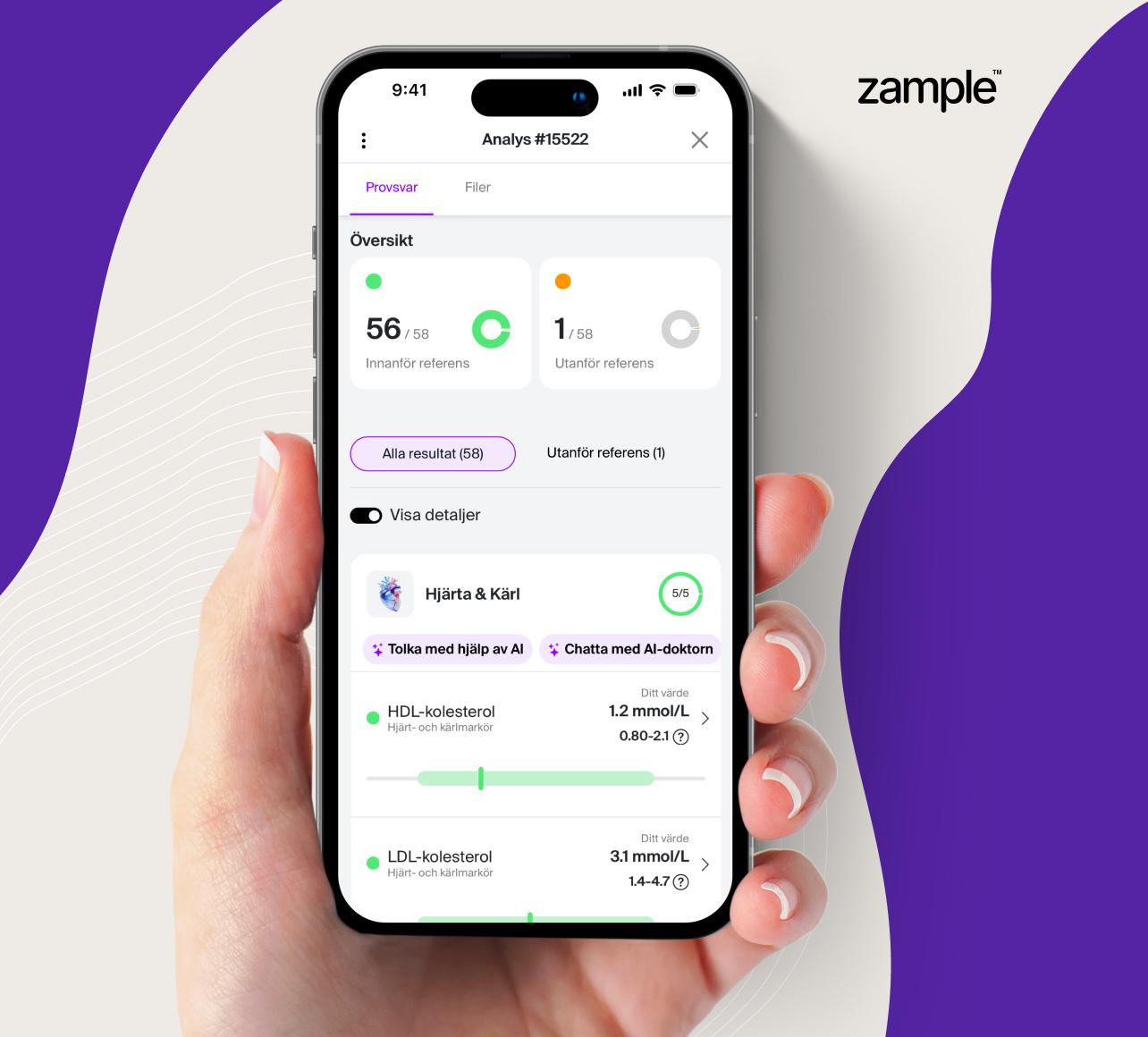
By measuring the levels of ferritin, a possible iron deficiency is detected if the result indicates that the availability of ferritin is low.
Ferritin deficiency indicates insufficient iron stored in the body and can lead to iron deficiency anemia. The consequences include fatigue, hair loss, difficulty concentrating, impaired immune function, increased risk of anemia during pregnancy and respiratory problems. It is important to monitor and treat ferritin deficiency to avoid these health problems.
Measuring ferritin levels can detect a possible iron deficiency if the results indicate that ferritin levels are low. Ferritin levels are especially important for people at risk, such as women of childbearing age, pregnant women, people with chronic diseases, and vegetarians or vegans. For these groups, early detection of iron deficiency can make a big difference to quality of life and overall health.
Why test your ferritin?
Analyzing ferritin levels can be important to:
- ✔️ Detect iron deficiency – Low ferritin can be an early sign of iron deficiency, which can lead to symptoms such as fatigue, dizziness, paleness and reduced physical performance.
- ✔️ Exclude iron deficiency – If you have symptoms similar to iron deficiency but normal ferritin levels, there may be another underlying cause for your symptoms.
- ✔️ Follow up iron status – If you have been treated for iron deficiency or are taking iron supplements, a ferritin test can help you check if your iron levels are improving.
- ✔️ Monitor iron overload – Elevated ferritin levels may indicate iron overload, which can be seen in conditions such as hemochromatosis or chronic inflammatory diseases.
Ferritin analysis in case of suspected iron deficiency
The ferritin test is particularly relevant for people who:
- Experience fatigue, dizziness or difficulty concentrating without a clear cause.
- Have anemia or suspected iron deficiency.
- Are pregnant or have heavy periods, which can increase the risk of iron deficiency.
- Are vegetarians or vegans and have a limited iron intake through their diet.
- Have an inflammatory disease or suspected iron overload.
How is the test performed?
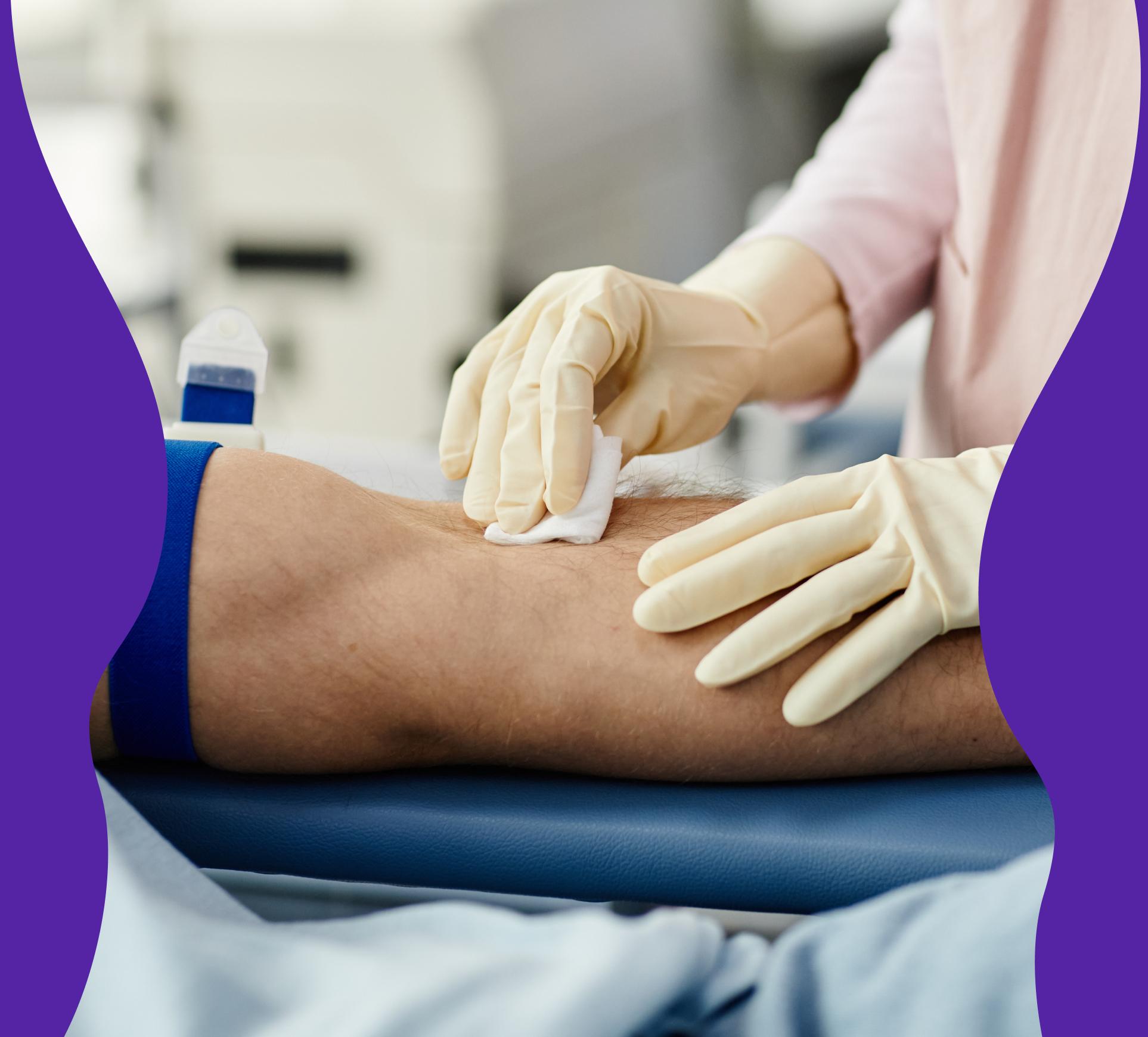
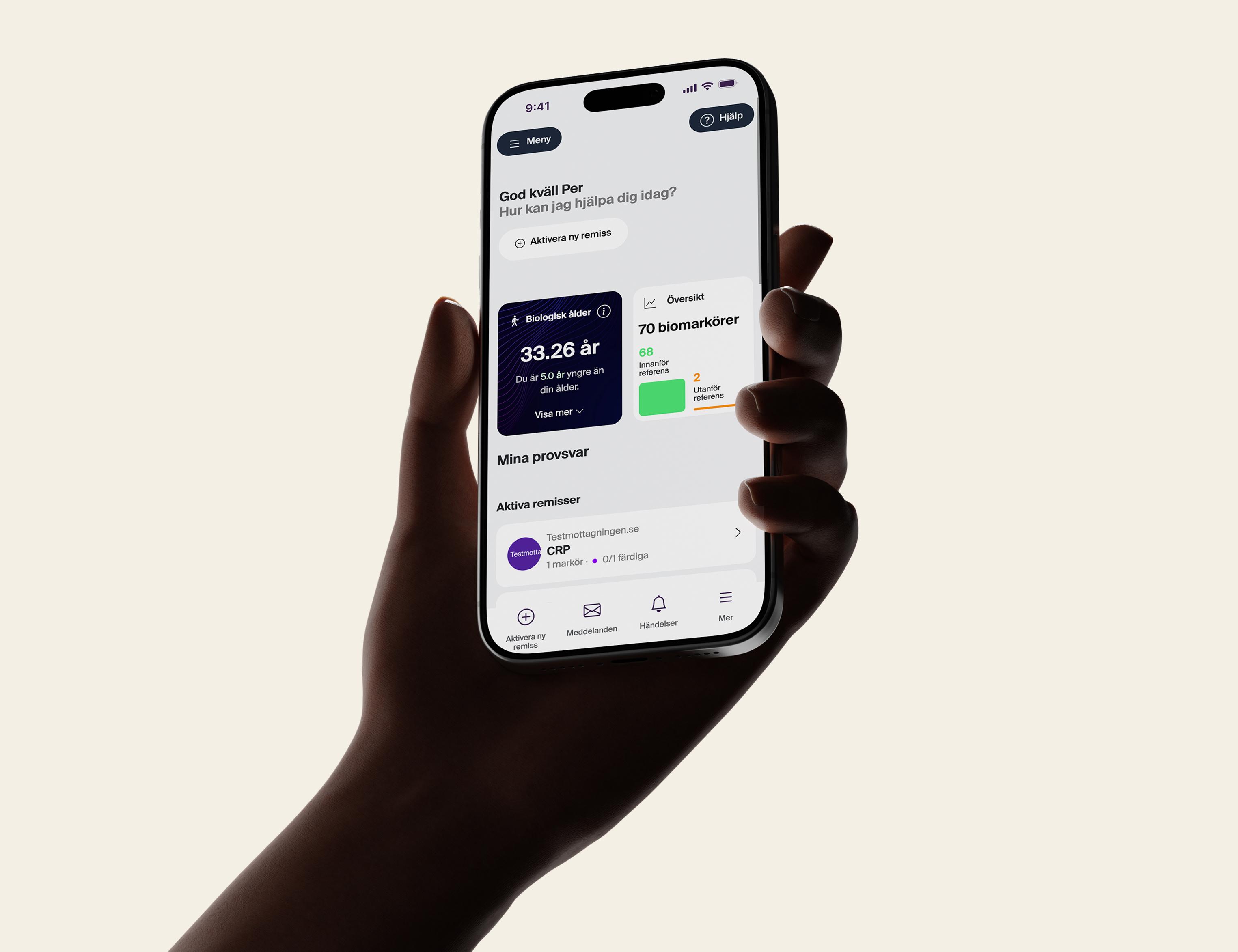
The test is performed through a venous blood sample taken by a healthcare professional and analyzed at an accredited laboratory. You will receive accurate values for your ferritin level, which will help you gain a better understanding of your iron status.
What affects ferritin levels in the body?
Ferritin levels are not only affected by iron intake, but also by the general condition of the body. Since ferritin is a so-called acute phase protein, the value can rise in the event of inflammation, infection or liver disease – even if you actually have low iron stores. This is important to know when interpreting the result.
Factors that can affect ferritin values include:
- Inflammation or infection: Ferritin may be elevated in temporary or chronic inflammatory conditions, such as rheumatism or intestinal diseases.
- Liver disease: Since ferritin is stored in the liver, the value can rise in liver damage or fatty liver.
- Overweight and metabolic syndrome: Elevated values are common in insulin resistance and low-grade inflammation.
- Pregnancy: Ferritin often drops during pregnancy as iron reserves are used for fetal development.
- Diet and alcohol: Low intake of iron-rich foods or excessive alcohol consumption can negatively affect levels.
To get a complete picture of your iron status Ferritin is often analyzed together with iron, transferrin and transferrin saturation. The combination of these values makes it possible to distinguish between iron deficiency, inflammation or iron overload (hemochromatosis).
High ferritin – not always too much iron
Elevated ferritin values are sometimes misinterpreted as iron overload, but in many cases it is due to the body reacting to inflammation or disease. Therefore, it is important to interpret the test in its context. If ferritin is elevated, additional markers such as CRP or transferrin saturation should be analyzed to distinguish between iron overload and inflammatory effects.