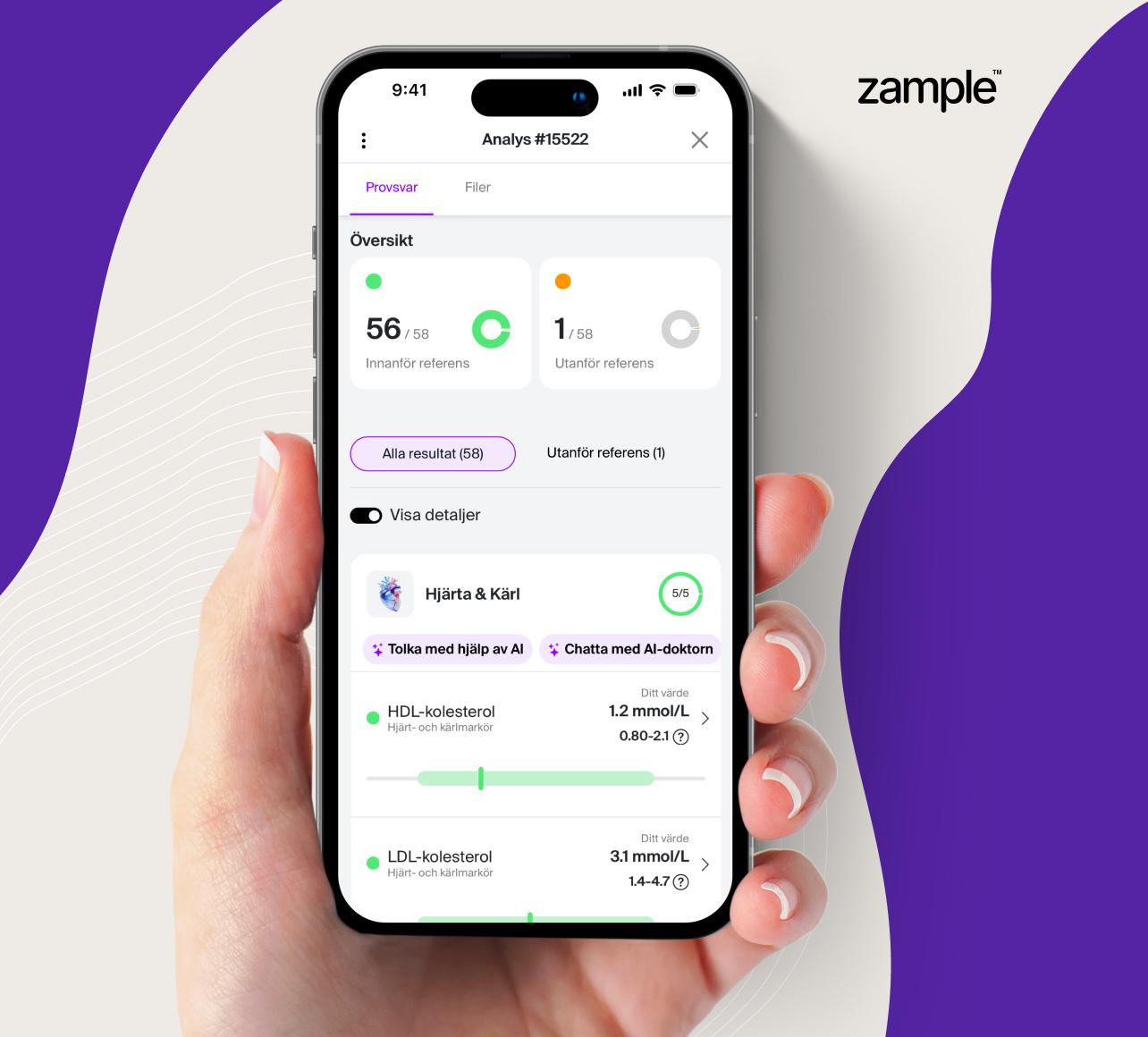
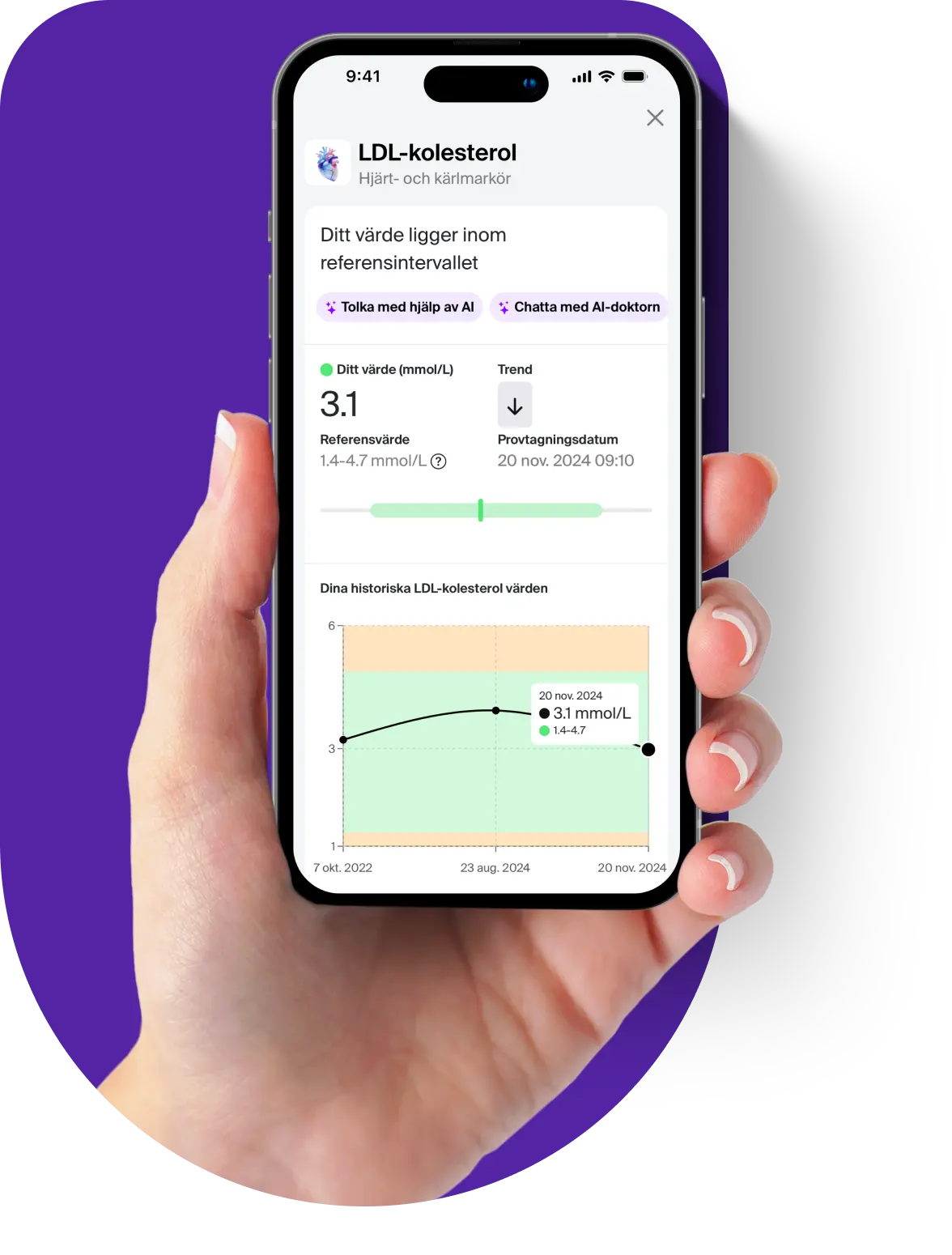
Venous blood test to analyze the concentration of CA 15-3, a tumor marker mainly used to monitor breast cancer. By analyzing CA 15-3 levels, doctors can get important information about the occurrence and progression of breast cancer and the effect of ongoing treatment. Elevated concentrations above 30 U/mL can also be seen in other forms of cancer and certain benign conditions.
The CA 15-3 test is used in several clinical situations where it is important to assess the presence or treatment of breast cancer. Common situations where the test is recommended include:
- Suspicion of breast cancer
- Follow-up of treatment for breast cancer
- Detected by recurrence of breast cancer
Elevated concentrations can also occur in:
- Breast cancer (up to 70% of cases)
- Liver cancer
- Colorectal cancer
- Ovarian cancer
When is a CA 15-3 test recommended?
Blood test for CA 15-3 is recommended when breast cancer is suspected or to monitor patients being treated for breast cancer. The test is used to assess the effect of the treatment and detect possible relapses. CA 15-3 levels may also be elevated in other cancers, such as liver cancer and colorectal cancer, as well as in certain benign conditions such as liver cirrhosis and inflammatory diseases.
Reference interval
Normal reference values for CA 15-3 are usually below 30 U/mL. Levels above this may indicate the presence of breast cancer or other diseases. It is important to note that reference values may vary depending on the laboratory and the method used to analyze CA 15-3, so test results should be interpreted with caution.
Reference Range
Normal reference values for CA 15-3 are usually below 30 U/mL. Levels above this may indicate the presence of breast cancer or other diseases. It is important to note that reference values may vary depending on the laboratory and the method used to analyze CA 15-3, so test results should be interpreted with caution.
Interpretation of CA 15-3 test results
Elevated test results above >30 U/mL of CA 15-3 most often occur in disseminated (metastatic) breast cancer, but they can also be seen in other diseases and conditions. However, abnormalities can be seen in various types of cancer, such as ovarian cancer, pancreatic cancer, prostate cancer, colorectal cancer, lung cancer, stomach cancer, cervical cancer, and uterine cancer. In addition, certain liver-related diseases such as cirrhosis and acute or chronic hepatitis can result in elevated values.