Vitamin E is a fat-soluble antioxidant that plays a key role in protecting the body's cells from harmful oxidative stress and free radicals. Vitamin E helps strengthen the immune system, supports nervous system functionality, and contributes to maintaining healthy skin and tissues. The most biologically active form of vitamin E, alpha-tocopherol, is not only the body's primary vitamin E but also a reliable marker for evaluating total vitamin E levels, upon which this test is based through a blood analysis of s-alpha-tocopherol.
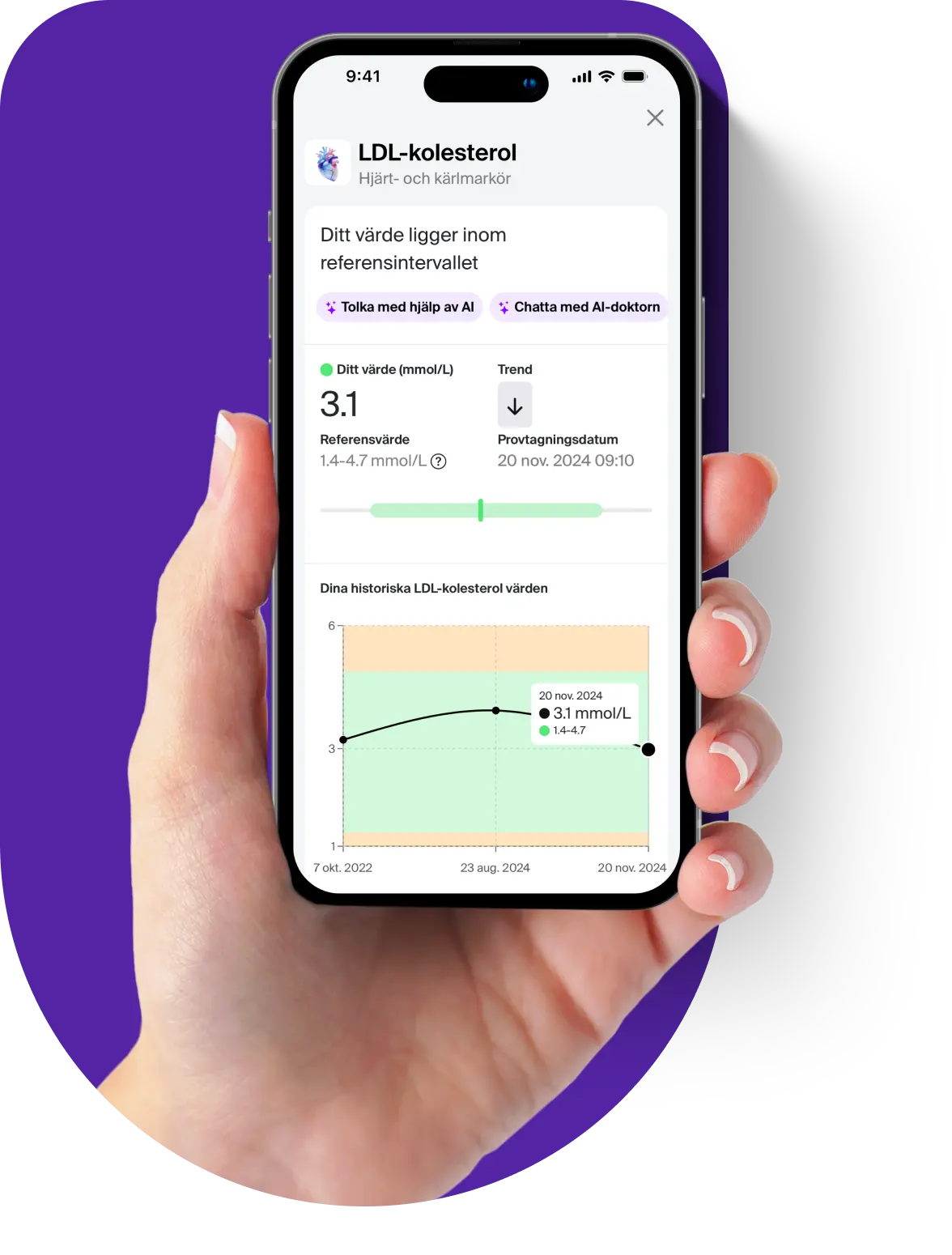
The analysis is based on s-alpha-tocopherol in the blood, the most common and biologically active form of vitamin E. This provides insight into your vitamin E levels and whether they fall within the normal reference range.
Insufficient vitamin E levels can affect the nervous system and muscle function, while excessive levels may negatively impact the blood's ability to clot.
Vitamin E deficiency is relatively rare but can occur in conjunction with certain conditions or factors that affect fat absorption. Testing for vitamin E may be particularly relevant if:
Vitamin E is essential for the body's functions and contributes to:
Normal levels of s-alpha-tocopherol range between 12–46 µmol/L. Low levels may indicate a vitamin E deficiency affecting nerve and muscle function, while high levels can suggest overdosage and an increased risk of bleeding.
```Before visiting a reception for sampling, you need to do the following:
Activate referral and select reception
To activate your referral, simply follow the instructions that you will receive via email after completing the purchase. The email contains an activation code, by clicking on the link in the email you enter the flow to fill in any information, activate the referral and select reception in the sample answer service zample.
Before the sampling
The referral is available digitally at the sampling unit after you activate it, follow the instructions you receive via email. Here you can read our guidelines before taking samples.
Lillåvägen 68, Bagarmossen
Edsbergs torg 1, Sollentuna
Fruängsgången 2, Hägersten
Södra Vägen 23, 1tr, Göteborg
Valhallavägen 91, Hus C, 1tr, Stockholm
Riddargatan 1, 1tr, Stockholm
Get control of your health - four simple steps
Choose a health check or create your own by adding optional health tests to your cart.
After payment, you will receive an activation code via email. Log in via "My test results" or click on the link in the email, and use the code to activate the referral and choose reception.
You visit the chosen reception to do your test. Your referral is valid for 5 months after activation.
You will receive your test answers within 1-5 working days, the test answers are received continuously. Once all test results are received, they are reviewed and issued by a doctor.
With us you always get:
Qualitative analysis
To offer you the highest possible quality and service we collaborate with accredited laboratories and trained healthcare personnel.
Lowest possible price
Our vision is that as many people as possible should have the opportunity to improve their health. That's why we always strive to keep prices low.
Your needs – your choice
With us, you can always choose freely among all our health markers and design your own personal health check based on your needs.
Quick test results – reviewed by doctors
Within 1-5 working days you will receive your test results, these are reviewed and assessed by a doctor. In the event of significantly deviating test answers, you will be called. You can also make an appointment with a doctor for a personal review.

Gives a blood test before a health check
Take health into your own hands
Understand what is happening in your body - with insight into your values, you can take control of your well-being and make any adjustments in your lifestyle.
A healthy and varied diet is said to be a trick to reduce the risk of ill health, with full insight into your health data you can see the balance of your vitamins, minerals and hormones.
Your lifestyle choices affect your general health, based on your values you can create the conditions for increased well-being - and a healthier life.
Yes, you can buy all tests and health checks with us for another person. After you complete a purchase, you will receive an email with an activation code. The activation code is not personal, which means that you can give the activation code to any person. The person who is to use the code needs to have a Swedish social security number or a valid reserve number.
Read moreNo, blood tests do not replace contact with the healthcare system, which together with medical history, clinical examinations and possible blood tests can make a diagnosis.
Read moreYou submit your test at any reception that is available all over Sweden, see the "receptions" tab in the menu. The sampling is carried out by trained healthcare personnel, so you can feel confident in your choice of sampling unit and in your meeting with the staff who work for them and who perform the sampling when you leave your blood sample intravenously. Analysis of your blood samples takes place at Sweden's leading accredited laboratory Synlab, Unilabs or Karolinska University Laboratory.
Read moreTo create your own referral select the specific markers you want to test for in the shopping cart. When you complete your purchase, a separate referral is created based on your choices.
Read moreIt usually takes 1-5 working days to get your test results, these are sent to you continuously as the analysis is done. The doctors comment will appear in the final report when all test results have been received, provided it is included in your analysis.
Read moreAdd the health check or tests you want to carry out to the shopping cart, go to checkout and choose the payment option that suits you. After completed payment, we will send an email with an activation code for your referral. You use the activation code in the sample response service "My journal" to activate the referral and select the reception where you want to leave your samples.
Read moreWith us you are always safe with our satisfied customer guarantee!