Folate, also known as vitamin B9, is a water-soluble vitamin that plays a central role in cell division, DNA synthesis, and the formation of red blood cells. Folate is especially important during periods of rapid growth, such as pregnancy and early childhood, as it contributes to fetal development and can help prevent neural tube defects. You naturally obtain folate through your diet, and if needed, the synthetic form of folate (folic acid) can be supplemented through fortified foods and dietary supplements.
Signs of Folate Deficiency
A deficiency in folate can cause a variety of symptoms, as the vitamin is involved in both blood formation and nerve function. Common signs of deficiency include:
- Fatigue and exhaustion
- Mucosal issues and mouth sores
- Hair loss
- Difficulty with concentration and memory
- Muscle and joint pain
- Slow-healing wounds
Prolonged folate deficiency can lead to megaloblastic anemia, where red blood cells become abnormally large and ineffective.
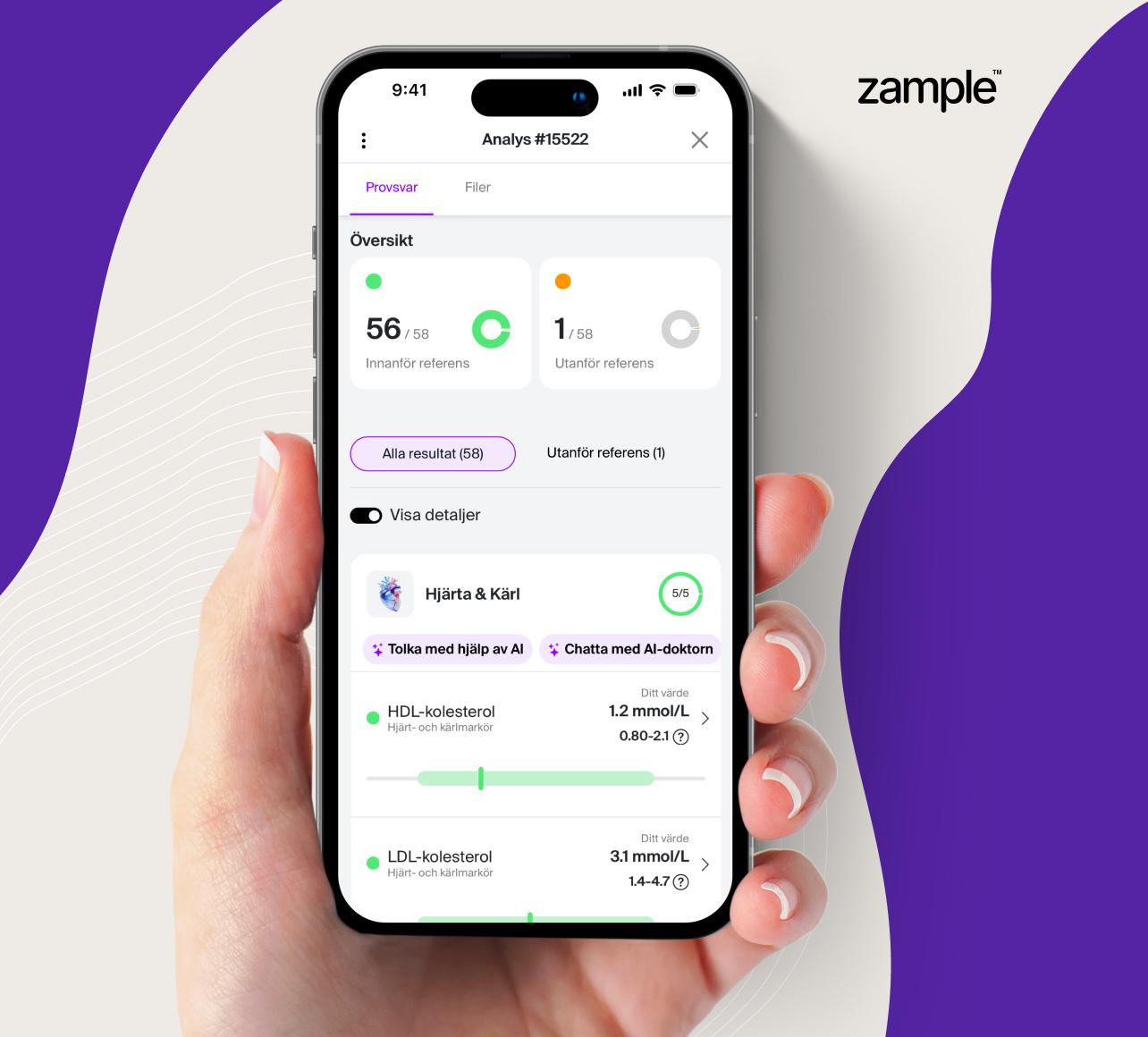
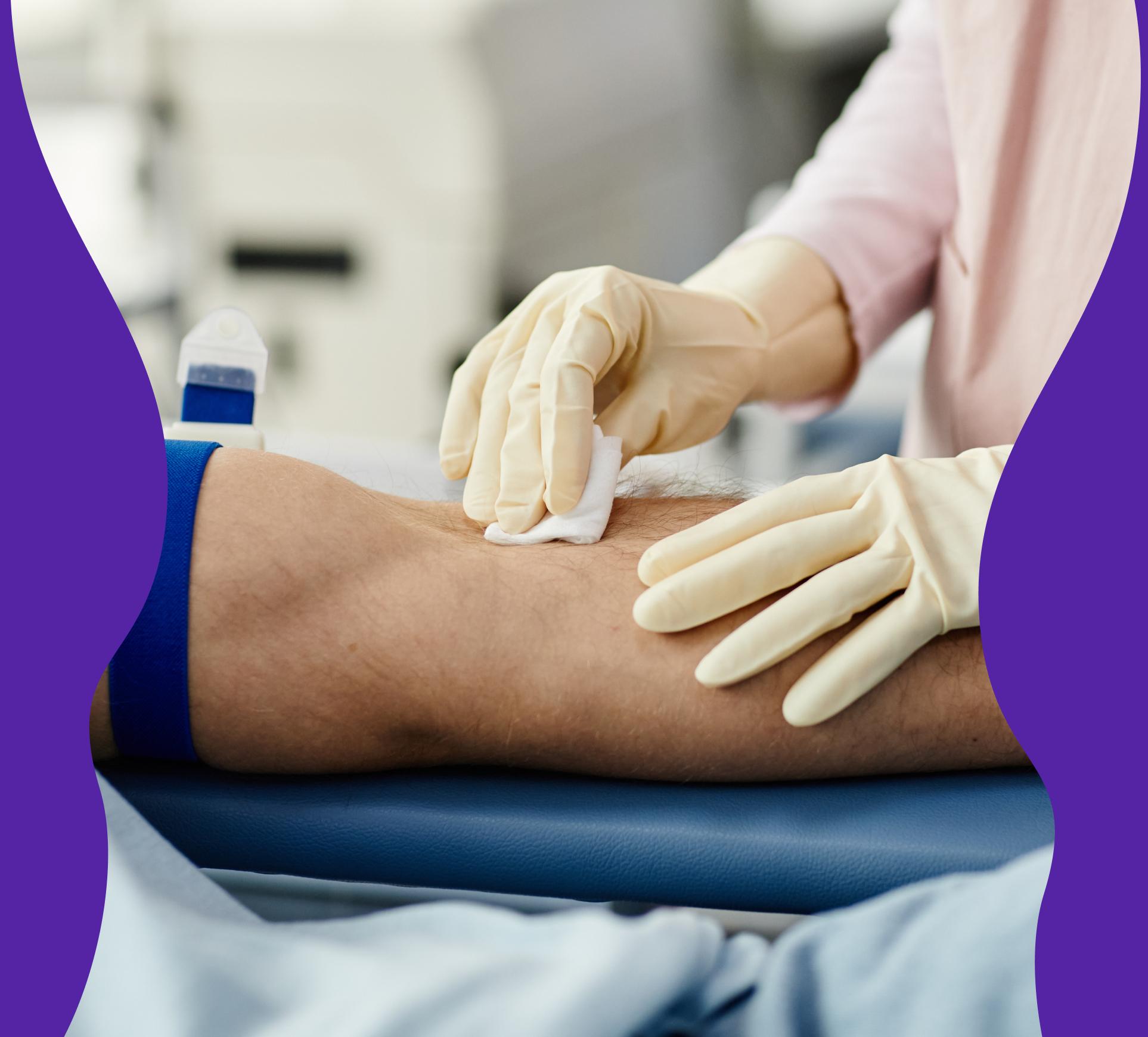
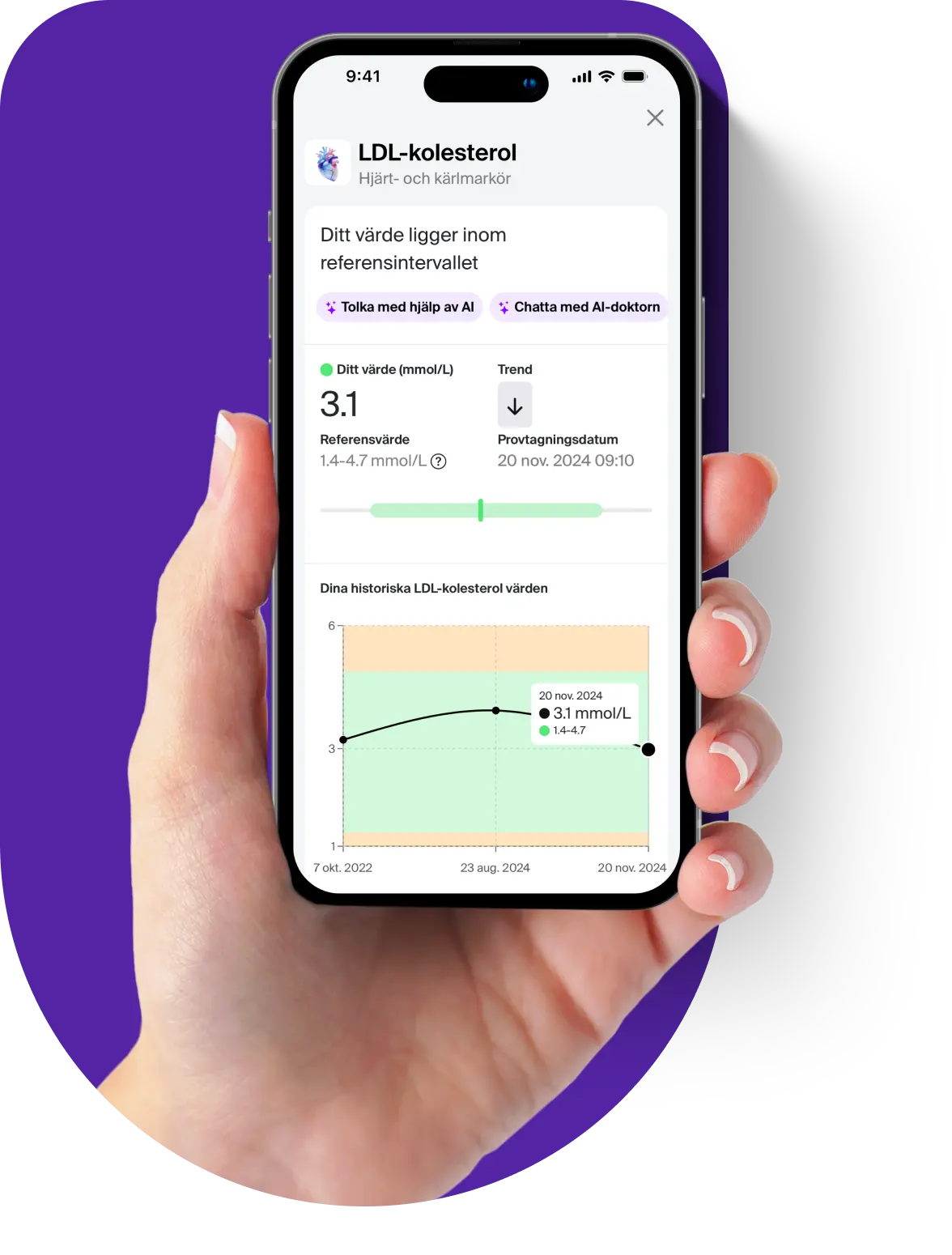
Suspect a folate deficiency? Order a test to check your levels.
Maintaining adequate folate (vitamin B9) levels is essential for blood formation, cell renewal, and overall health. A blood test to measure folate levels may be particularly relevant if you:
- Are pregnant or planning to become pregnant, as folate is crucial for fetal development.
- Have a limited or nutrient-poor diet that may lead to deficiency.
- Have digestive disorders such as celiac disease or Crohn’s disease, which can affect folate absorption.
- Have low blood counts or suspect anemia.
- Experience unexplained fatigue, dizziness, or difficulty concentrating.
- Consume high amounts of alcohol, which can impair the body’s ability to absorb folate.
If you recognize yourself in any of these points, a folate test can provide valuable insight into your health status.
Folate and Pregnancy
During pregnancy, adequate folate intake is crucial for fetal development. Low folate levels increase the risk of neural tube defects, such as spina bifida. For this reason, women are advised to take folic acid supplements before conception and during the first 12 weeks of pregnancy.
The Difference Between Folate and Folic Acid
Folate and folic acid are two different forms of vitamin B9. Folate is the natural form found in food, while folic acid is the synthetic form used in supplements and fortified products. The body converts folic acid into its active form (5-MTHF), but this process can be inefficient in some individuals due to genetic variations.